Plant-Produced Glycosylated and In Vivo Deglycosylated Receptor Binding Domain Proteins of SARS-CoV-2 Induce Potent Neutralizing Responses in Mice
- PMID: 34452461
- PMCID: PMC8402646
- DOI: 10.3390/v13081595
Plant-Produced Glycosylated and In Vivo Deglycosylated Receptor Binding Domain Proteins of SARS-CoV-2 Induce Potent Neutralizing Responses in Mice
Abstract
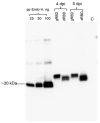
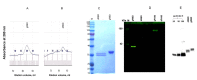
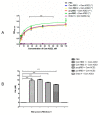
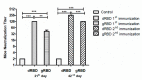
The COVID-19 pandemic, caused by SARS-CoV-2, has rapidly spread to more than 222 countries and has put global public health at high risk. The world urgently needs cost-effective and safe SARS-CoV-2 vaccines, antiviral, and therapeutic drugs to control it. In this study, we engineered the receptor binding domain (RBD) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) protein and produced it in the plant Nicotiana benthamiana in a glycosylated and deglycosylated form. Expression levels of both glycosylated (gRBD) and deglycosylated (dRBD) RBD were greater than 45 mg/kg fresh weight. The purification yields were 22 mg of pure protein/kg of plant biomass for gRBD and 20 mg for dRBD, which would be sufficient for commercialization of these vaccine candidates. The purified plant-produced RBD protein was recognized by an S protein-specific monoclonal antibody, demonstrating specific reactivity of the antibody to the plant-produced RBD proteins. The SARS-CoV-2 RBD showed specific binding to angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), the SARS-CoV-2 receptor. In mice, the plant-produced RBD antigens elicited high titers of antibodies with a potent virus-neutralizing activity. To our knowledge, this is the first report demonstrating that mice immunized with plant-produced deglycosylated RBD form elicited high titer of RBD-specific antibodies with potent neutralizing activity against SARS-CoV-2 infection. Thus, obtained data support that plant-produced glycosylated and in vivo deglycosylated RBD antigens, developed in this study, are promising vaccine candidates for the prevention of COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; plant; receptor binding domain (RBD) vaccine; spike protein; transient expression system.
Conflict of interest statement
T.M. is named as the inventor on the patent applications covering plant-produced COVID-19 vaccine development.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Isolation and Characterization of Mouse Monoclonal Antibodies That Neutralize SARS-CoV-2 and Its Variants of Concern Alpha, Beta, Gamma and Delta by Binding Conformational Epitopes of Glycosylated RBD With High Potency.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 26;12:750386. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.750386. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34764961 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid production of SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain (RBD) and spike specific monoclonal antibody CR3022 in Nicotiana benthamiana.Sci Rep. 2020 Oct 19;10(1):17698. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-74904-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33077899 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Basis of a Human Neutralizing Antibody Specific to the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein Receptor-Binding Domain.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Oct 31;9(2):e0135221. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.01352-21. Epub 2021 Oct 13. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34643438 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain by neutralizing antibodies.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021 Jan 29;538:192-203. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.10.012. Epub 2020 Oct 10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021. PMID: 33069360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor binding domain and their delicate balance between ACE2 affinity and antibody evasion.Protein Cell. 2024 May 28;15(6):403-418. doi: 10.1093/procel/pwae007. Protein Cell. 2024. PMID: 38442025 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Theaflavin 3-gallate inhibits the main protease (Mpro) of SARS-CoV-2 and reduces its count in vitro.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 30;12(1):13146. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17558-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35908093 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating Constraints Along the Plant Secretory Pathway to Improve Production of a SARS-CoV-2 Spike Vaccine Candidate.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jan 4;12:798822. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.798822. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35058959 Free PMC article.
-
Production and Characterization of Nucleocapsid and RBD Cocktail Antigens of SARS-CoV-2 in Nicotiana benthamiana Plant as a Vaccine Candidate against COVID-19.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Nov 17;9(11):1337. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9111337. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34835268 Free PMC article.
-
Plant production of recombinant antigens containing the receptor binding domain (RBD) of two SARS-CoV-2 variants.Biotechnol Lett. 2024 Dec;46(6):1303-1318. doi: 10.1007/s10529-024-03517-9. Epub 2024 Jul 27. Biotechnol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39066957
-
Transient Expression of Glycosylated SARS-CoV-2 Antigens in Nicotiana benthamiana.Plants (Basel). 2022 Apr 18;11(8):1093. doi: 10.3390/plants11081093. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35448821 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

