Regulation of RNA Interference Pathways in the Insect Vector Laodelphax striatellus by Viral Proteins of Rice Stripe Virus
- PMID: 34452456
- PMCID: PMC8402809
- DOI: 10.3390/v13081591
Regulation of RNA Interference Pathways in the Insect Vector Laodelphax striatellus by Viral Proteins of Rice Stripe Virus
Abstract
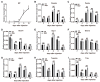
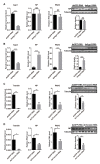
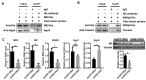
RNA interference (RNAi), especially the small interfering RNA (siRNA) and microRNA (miRNA) pathways, plays an important role in defending against viruses in plants and insects. However, how insect-transmitted phytoviruses regulate the RNAi-mediated antiviral response in vector insects has barely been uncovered. In this study, we explored the interaction between rice stripe virus (RSV) and the miRNA and siRNA pathways of the small brown planthopper, which is a vector insect. The transcript and protein levels of key genes in the two RNAi pathways did not change during the RSV infection process. When the expression of insect Ago1, Ago2, or Translin was silenced by the injection of double-stranded RNAs targeting these genes, viral replication was promoted with Ago2 silencing but inhibited with Translin silencing. Protein-protein binding assays showed that viral NS2 and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase interacted with insect Ago2 and Translin, respectively. When NS2 was knocked down, the transcript level of Ago2 increased and viral replication was inhibited. Therefore, viral NS2 behaved like an siRNA suppressor in vector insects. This protein-binding regulation of insect RNAi systems reflects a complicated and diverse coevolution of viruses with their vector insects.
Keywords: Ago2; miRNA; planthopper; rice stripe virus; siRNA; translin; viral replication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rice stripe virus-derived siRNAs play different regulatory roles in rice and in the insect vector Laodelphax striatellus.BMC Plant Biol. 2018 Oct 4;18(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1438-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2018. PMID: 30286719 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative Splicing Landscape of Small Brown Planthopper and Different Response of JNK2 Isoforms to Rice Stripe Virus Infection.J Virol. 2022 Jan 26;96(2):e0171521. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01715-21. Epub 2021 Nov 10. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 34757837 Free PMC article.
-
Potential functional pathways of plant RNA virus-derived small RNAs in a vector insect.Methods. 2020 Nov 1;183:38-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2019.10.006. Epub 2019 Oct 22. Methods. 2020. PMID: 31654749
-
The small brown planthopper (Laodelphax striatellus) as a vector of the rice stripe virus.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2023 Feb;112(2):e21992. doi: 10.1002/arch.21992. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36575628 Review.
-
RNA Interference in Insects: Protecting Beneficials and Controlling Pests.Front Physiol. 2019 Jan 11;9:1912. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01912. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30687124 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction between endogenous microRNAs and virus-derived small RNAs controls viral replication in insect vectors.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Jul 7;18(7):e1010709. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010709. eCollection 2022 Jul. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35797383 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

