Transcription Control of Liver Development
- PMID: 34440795
- PMCID: PMC8391549
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10082026
Transcription Control of Liver Development
Abstract
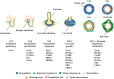
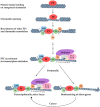
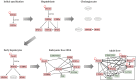
During liver organogenesis, cellular transcriptional profiles are constantly reshaped by the action of hepatic transcriptional regulators, including FoxA1-3, GATA4/6, HNF1α/β, HNF4α, HNF6, OC-2, C/EBPα/β, Hex, and Prox1. These factors are crucial for the activation of hepatic genes that, in the context of compact chromatin, cannot access their targets. The initial opening of highly condensed chromatin is executed by a special class of transcription factors known as pioneer factors. They bind and destabilize highly condensed chromatin and facilitate access to other "non-pioneer" factors. The association of target genes with pioneer and non-pioneer transcription factors takes place long before gene activation. In this way, the underlying gene regulatory regions are marked for future activation. The process is called "bookmarking", which confers transcriptional competence on target genes. Developmental bookmarking is accompanied by a dynamic maturation process, which prepares the genomic loci for stable and efficient transcription. Stable hepatic expression profiles are maintained during development and adulthood by the constant availability of the main regulators. This is achieved by a self-sustaining regulatory network that is established by complex cross-regulatory interactions between the major regulators. This network gradually grows during liver development and provides an epigenetic memory mechanism for safeguarding the optimal expression of the regulators.
Keywords: bookmarking; chromatin; development; gene expression; liver; transcription factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bookmarking by Non-pioneer Transcription Factors during Liver Development Establishes Competence for Future Gene Activation.Cell Rep. 2020 Feb 4;30(5):1319-1328.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.01.006. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32023452 Free PMC article.
-
Homeobox gene Hex is essential for onset of mouse embryonic liver development and differentiation of the monocyte lineage.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000 Oct 5;276(3):1155-61. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.3548. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000. PMID: 11027604
-
Gene regulation by homeobox transcription factor Prox1 in murine hepatoblasts.Cell Tissue Res. 2007 Nov;330(2):209-20. doi: 10.1007/s00441-007-0477-4. Epub 2007 Sep 9. Cell Tissue Res. 2007. PMID: 17828556
-
Transcriptional Control: A Directional Sign at the Crossroads of Adult Hepatic Progenitor Cells' Fates.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Jun 24;20(9):3544-3556. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.93739. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38993564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pioneer factors, genetic competence, and inductive signaling: programming liver and pancreas progenitors from the endoderm.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2008;73:119-26. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2008.73.040. Epub 2008 Nov 21. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2008. PMID: 19028990 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LOX-1 attenuates high glucose-induced autophagy via AMPK/HNF4α signaling in HLSECs.Heliyon. 2022 Dec 17;8(12):e12385. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e12385. eCollection 2022 Dec. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36590506 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Provides Novel Molecular Events for the Differentiation and Maturation of Hepatocytes during the Liver Development of Zebrafish.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 13;10(9):2264. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092264. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36140365 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating, cell-free methylated DNA indicates cellular sources of allograft injury after liver transplant.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 5:2024.04.04.588176. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.04.588176. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38617373 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Single-Cell RNA Sequencing of Sox17-Expressing Lineages Reveals Distinct Gene Regulatory Networks and Dynamic Developmental Trajectories.Stem Cells. 2023 Jun 15;41(6):643-657. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxad030. Stem Cells. 2023. PMID: 37085274 Free PMC article.
-
The role of FOXA family transcription factors in glucolipid metabolism and NAFLD.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 31;14:1081500. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1081500. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36798663 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

