Connexin 43 and Sonic Hedgehog Pathway Interplay in Glioblastoma Cell Proliferation and Migration
- PMID: 34439999
- PMCID: PMC8389699
- DOI: 10.3390/biology10080767
Connexin 43 and Sonic Hedgehog Pathway Interplay in Glioblastoma Cell Proliferation and Migration
Abstract
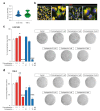
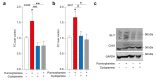
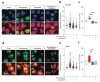
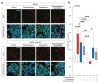
Glioblastoma (GBM) represents the most common primary brain tumor within the adult population. Current therapeutic options are still limited by high rate of recurrences and signalling axes that promote GBM aggressiveness. The contribution of gap junctions (GJs) to tumor growth and progression has been proven by experimental evidence. Concomitantly, tumor microenvironment has received increasing interest as a critical process in dysregulation and homeostatic escape, finding a close link between molecular mechanisms involved in connexin 43 (CX43)-based intercellular communication and tumorigenesis. Moreover, evidence has come to suggest a crucial role of sonic hedgehog (SHH) signalling pathway in GBM proliferation, cell fate and differentiation. Herein, we used two human GBM cell lines, modulating SHH signalling and CX43-based intercellular communication in in vitro models using proliferation and migration assays. Our evidence suggests that modulation of the SHH effector smoothened (SMO), by using a known agonist (i.e., purmorphamine) and a known antagonist (i.e., cyclopamine), affects the CX43 expression levels and therefore the related functions. Moreover, SMO activation also increased cell proliferation and migration. Importantly, inhibition of CX43 channels was able to prevent SMO-induced effects. SHH pathway and CX43 interplay acts inducing tumorigenic program and supporting cell migration, likely representing druggable targets to develop new therapeutic strategies for GBM.
Keywords: GBM; GLI1; connexin; gap junction; smoothened.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulation of Sonic hedgehog signaling and WW domain containing oxidoreductase WOX1 expression enhances radiosensitivity of human glioblastoma cells.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015 Mar;240(3):392-9. doi: 10.1177/1535370214565989. Epub 2015 Jan 16. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015. PMID: 25595187 Free PMC article.
-
Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Mediates Proliferation and Migration of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis via MAPK/ERK Signaling Pathway.Front Immunol. 2018 Dec 5;9:2847. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02847. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30568656 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of KIF3A in patient-derived glioblastoma cells: effects on ciliogenesis, hedgehog sensitivity, and tumorigenesis.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 9;7(6):7029-43. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6854. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26760767 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Pathway: Review of Smoothened and GLI Inhibitors.Cancers (Basel). 2016 Feb 15;8(2):22. doi: 10.3390/cancers8020022. Cancers (Basel). 2016. PMID: 26891329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small-molecule modulators of the Sonic Hedgehog signaling pathway.Mol Biosyst. 2010 Jan;6(1):44-54. doi: 10.1039/b910196a. Epub 2009 Aug 27. Mol Biosyst. 2010. PMID: 20024066 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigational Microbiological Therapy for Glioma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 2;14(23):5977. doi: 10.3390/cancers14235977. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36497459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Glioblastoma Stem Cells to Overcome Chemoresistance: An Overview of Current Therapeutic Strategies.Biomedicines. 2022 Jun 2;10(6):1308. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061308. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anaplastic thyroid cancer cells reduce CD71 levels to increase iron overload tolerance.J Transl Med. 2023 Nov 3;21(1):780. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04664-9. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37924062 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog Morphogens Act as Growth Factors Critical to Pre- and Postnatal Cardiac Development and Maturation: How Primary Cilia Mediate Their Signal Transduction.Cells. 2022 Jun 9;11(12):1879. doi: 10.3390/cells11121879. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35741008 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IGFBP-6/sonic hedgehog/TLR4 signalling axis drives bone marrow fibrotic transformation in primary myelofibrosis.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Dec 14;13(23):25055-25071. doi: 10.18632/aging.203779. Epub 2021 Dec 14. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34905501 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wen P.Y., Weller M., Lee E.Q., Alexander B.M., Barnholtz-Sloan J.S., Barthel F.P., Batchelor T.T., Bindra R.S., Chang S.M., Chiocca E.A., et al. Glioblastoma in adults: A Society for Neuro-Oncology (SNO) and European Society of Neuro-Oncology (EANO) consensus review on current management and future directions. Neuro Oncol. 2020;22:1073–1113. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noaa106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Verhaak R.G., Hoadley K.A., Purdom E., Wang V., Qi Y., Wilkerson M.D., Miller C.R., Ding L., Golub T., Mesirov J.P., et al. Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell. 2010;17:98–110. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2009.12.020. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

