Transcriptome and Literature Mining Highlight the Differential Expression of ERLIN1 in Immune Cells during Sepsis
- PMID: 34439987
- PMCID: PMC8389572
- DOI: 10.3390/biology10080755
Transcriptome and Literature Mining Highlight the Differential Expression of ERLIN1 in Immune Cells during Sepsis
Abstract
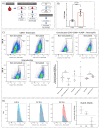
Sepsis results from the dysregulation of the host immune system. This highly variable disease affects 19 million people globally, and accounts for 5 million deaths annually. In transcriptomic datasets curated from public repositories, we observed a consistent upregulation (3.26-5.29 fold) of ERLIN1-a gene coding for an ER membrane prohibitin and a regulator of inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate receptors and sterol regulatory element-binding proteins-under septic conditions in healthy neutrophils, monocytes, and whole blood. In vitro expression of the ERLIN1 gene and proteins was measured by stimulating the whole blood of healthy volunteers to a combination of lipopolysaccharide and peptidoglycan. Septic stimulation induced a significant increase in ERLIN1 expression; however, ERLIN1 was differentially expressed among the immune blood cell subsets. ERLIN1 was uniquely increased in whole blood neutrophils, and confirmed in the differentiated HL60 cell line. The scarcity of ERLIN1 in sepsis literature indicates a knowledge gap between the functions of ERLIN1, calcium homeostasis, and cholesterol and fatty acid biosynthesis, and sepsis. In combination with experimental data, we bring forth the hypothesis that ERLIN1 is variably modulated among immune cells in response to cellular perturbations, and has implications for ER functions and/or ER membrane protein components during sepsis.
Keywords: bacteremia; calcium channel; cholesterol biosynthesis; immunometabolism; innate immunity; leukocytes; myeloid cells; neutrophil; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The erlin2 T65I mutation inhibits erlin1/2 complex-mediated inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor ubiquitination and phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate binding.J Biol Chem. 2018 Oct 5;293(40):15706-15714. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004547. Epub 2018 Aug 22. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30135210 Free PMC article.
-
Binding of the erlin1/2 complex to the third intralumenal loop of IP3R1 triggers its ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation.J Biol Chem. 2022 Jun;298(6):102026. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102026. Epub 2022 May 11. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35568199 Free PMC article.
-
Raft-like lipid microdomains drive autophagy initiation via AMBRA1-ERLIN1 molecular association within MAMs.Autophagy. 2021 Sep;17(9):2528-2548. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1834207. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Autophagy. 2021. PMID: 33034545 Free PMC article.
-
A novel homozygous mutation in ERLIN1 gene causing spastic paraplegia 62 and literature review.Eur J Med Genet. 2022 Nov;65(11):104608. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2022.104608. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Eur J Med Genet. 2022. PMID: 36100157 Review.
-
Annexin A3 in sepsis: novel perspectives from an exploration of public transcriptome data.Immunology. 2020 Dec;161(4):291-302. doi: 10.1111/imm.13239. Epub 2020 Aug 31. Immunology. 2020. PMID: 32682335 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomics analysis of lung tissue reveals protein makers for the lung injury of adjuvant arthritis rats.Mol Med Rep. 2023 Sep;28(3):163. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2023.13051. Epub 2023 Jul 14. Mol Med Rep. 2023. PMID: 37449522 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid oxidation dysregulation: an emerging player in the pathophysiology of sepsis.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 3;14:1224335. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1224335. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37600769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomic profile investigations highlight a putative role for NUDT16 in sepsis.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Mar;26(5):1714-1721. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17240. Epub 2022 Feb 17. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35174610 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals the Pathogenesis of Growth-Disordered Raccoon Dog.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 18;24(18):14237. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814237. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762538 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

