High HbA1c is a risk factor for complications after hepatectomy and influences for hepatocellular carcinoma without HBV and HCV infection
- PMID: 34430524
- PMCID: PMC8350996
- DOI: 10.21037/hbsn.2020.01.03
High HbA1c is a risk factor for complications after hepatectomy and influences for hepatocellular carcinoma without HBV and HCV infection
Abstract
Background: Currently, the population with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) is increasing worldwide. However, the influence of DM or hyperglycemia on the outcome of resected hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is unclear.
Methods: We analyzed 756 patients with HCC who underwent hepatectomy. These patients were assigned to an HbA1c ≥7.0% (H-A1c; n=100) or HbA1c <7.0% (L-A1c; n=656) group depending on their HbA1c level at admission. We investigated prognoses, clinicopathological characteristics and surgical outcomes including morbidities of HCC patients with high HbA1c, prognoses according to the treatment for DM were also investigated.
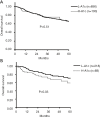
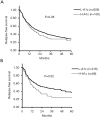
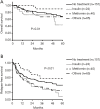
Results: Among all patients and those with hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection, overall survival (OS) and relapse-free survival (RFS) did not differ significantly between the H-A1c and L-A1c groups. In contrast, the 5-year OS rate of the H-A1c group was 55% and that of the L-A1c group 71% among patients without HBV and HCV (NBNC patients) (P=0.03). Among NBNC patients, the median RFS of the H-A1c group was 13 months, and that of the L-A1c group was 26 months (P=0.02). In addition, metformin use was an independent favorable factor for both OS and RFS. The H-A1c group had significantly higher rates of hyperbilirubinemia, wound infection, and pneumonia.
Conclusions: HCC patients with high HbA1c might have poor prognoses for both survival and recurrence in NBNC-HCC. High HbA1c may also be a risk factor for morbidities after hepatectomy. Metformin use may constitute a good option for NBNC patients with HCC.
Keywords: HbA1c; Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); diabetes mellitus (DM); hepatectomy; metformin.
2021 Hepatobiliary Surgery and Nutrition. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/hbsn.2020.01.03). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparison of the surgical outcomes among patients with HBV-positive, HCV-positive, and non-B non-C hepatocellular carcinoma: a nationwide study of 11,950 patients.Ann Surg. 2015 Mar;261(3):513-20. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000821. Ann Surg. 2015. PMID: 25072437
-
Postoperative Outcomes for Patients with Non-B Non-C Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Subgroup Analysis of Patients with a History of Hepatitis B Infection.Ann Surg Oncol. 2015 Dec;22 Suppl 3:S1034-40. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4845-0. Epub 2015 Sep 8. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26350363
-
Comparison of clinicopathologic characteristics among patients with HBV-positive, HCV-positive and Non-B Non-C hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2023 Aug 23;23(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s12876-023-02925-x. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 37612653 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of viral hepatitis status on prognosis in patients undergoing hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis of observational studies.World J Surg Oncol. 2011 Sep 21;9:108. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-9-108. World J Surg Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21933440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of diabetes mellitus and effectiveness of metformin on hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatol Res. 2023 Jul;53(7):579-594. doi: 10.1111/hepr.13912. Epub 2023 May 30. Hepatol Res. 2023. PMID: 37154478 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors Use with Reduced Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with Chronic HBV Infection.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 10;15(4):1148. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041148. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831491 Free PMC article.
-
Letter to the Editor: Inflammation influences the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Int J Clin Oncol. 2022 Nov;27(11):1791-1792. doi: 10.1007/s10147-022-02234-5. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Int J Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35962254 No abstract available.
-
Time-restricted feeding: what we have done and what more we can do?Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2023 Jun 1;12(3):440-442. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-23-246. Epub 2023 May 22. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37351146 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Association of perioperative use of statins, metformin, and aspirin with recurrence after curative liver resection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A propensity score matching analysis.Cancer Med. 2023 Oct;12(19):19548-19559. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6569. Epub 2023 Sep 22. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 37737550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes atlas. Diabetes atlas. 2015. Available online: http://www.idf.org/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
