Formation of artificial chromosomes in Caenorhabditis elegans and analyses of their segregation in mitosis, DNA sequence composition and holocentromere organization
- PMID: 34417622
- PMCID: PMC8450109
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkab690
Formation of artificial chromosomes in Caenorhabditis elegans and analyses of their segregation in mitosis, DNA sequence composition and holocentromere organization
Abstract
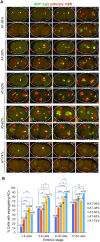
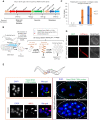
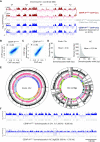
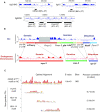
To investigate how exogenous DNA concatemerizes to form episomal artificial chromosomes (ACs), acquire equal segregation ability and maintain stable holocentromeres, we injected DNA sequences with different features, including sequences that are repetitive or complex, and sequences with different AT-contents, into the gonad of Caenorhabditis elegans to form ACs in embryos, and monitored AC mitotic segregation. We demonstrated that AT-poor sequences (26% AT-content) delayed the acquisition of segregation competency of newly formed ACs. We also co-injected fragmented Saccharomyces cerevisiae genomic DNA, differentially expressed fluorescent markers and ubiquitously expressed selectable marker to construct a less repetitive, more complex AC. We sequenced the whole genome of a strain which propagates this AC through multiple generations, and de novo assembled the AC sequences. We discovered CENP-AHCP-3 domains/peaks are distributed along the AC, as in endogenous chromosomes, suggesting a holocentric architecture. We found that CENP-AHCP-3 binds to the unexpressed marker genes and many fragmented yeast sequences, but is excluded in the yeast extremely high-AT-content centromeric and mitochondrial DNA (> 83% AT-content) on the AC. We identified A-rich motifs in CENP-AHCP-3 domains/peaks on the AC and on endogenous chromosomes, which have some similarity with each other and similarity to some non-germline transcription factor binding sites.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
RbAp46/48LIN-53 and HAT-1 are required for initial CENP-AHCP-3 deposition and de novo holocentromere formation on artificial chromosomes in Caenorhabditis elegans embryos.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Sep 20;49(16):9154-9173. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab217. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33872374 Free PMC article.
-
Histone H3K9 and H4 Acetylations and Transcription Facilitate the Initial CENP-AHCP-3 Deposition and De Novo Centromere Establishment in Caenorhabditis elegans Artificial Chromosomes.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2018 Apr 13;11(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13072-018-0185-1. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2018. PMID: 29653589 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and analysis of artificial chromosomes with de novo holocentromeres in Caenorhabditis elegans.Essays Biochem. 2020 Sep 4;64(2):233-249. doi: 10.1042/EBC20190067. Essays Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32756873 Review.
-
"Lessons from the extremes: Epigenetic and genetic regulation in point monocentromere and holocentromere establishment on artificial chromosomes".Exp Cell Res. 2020 May 15;390(2):111974. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.111974. Epub 2020 Mar 26. Exp Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32222413 Review.
-
RbAp46/48(LIN-53) Is Required for Holocentromere Assembly in Caenorhabditis elegans.Cell Rep. 2016 Mar 1;14(8):1819-28. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.01.065. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 26904949
Cited by
-
Modular safe-harbor transgene insertion for targeted single-copy and extrachromosomal array integration in Caenorhabditis elegans.G3 (Bethesda). 2022 Aug 25;12(9):jkac184. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac184. G3 (Bethesda). 2022. PMID: 35900171 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput library transgenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans via Transgenic Arrays Resulting in Diversity of Integrated Sequences (TARDIS).Elife. 2023 Jul 4;12:RP84831. doi: 10.7554/eLife.84831. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37401921 Free PMC article.
-
Nematode chromosomes.Genetics. 2022 May 5;221(1):iyac014. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac014. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 35323874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recurrent but Short-Lived Duplications of Centromeric Proteins in Holocentric Caenorhabditis Species.Mol Biol Evol. 2022 Oct 7;39(10):msac206. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msac206. Mol Biol Evol. 2022. PMID: 36173809 Free PMC article.
-
Argonaute protein CSR-1 restricts localization of holocentromere protein HCP-3, the C. elegans CENP-A homolog.J Cell Sci. 2024 Sep 15;137(18):jcs261895. doi: 10.1242/jcs.261895. Epub 2024 Sep 18. J Cell Sci. 2024. PMID: 39037215 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

