Fc Galactosylation Promotes Hexamerization of Human IgG1, Leading to Enhanced Classical Complement Activation
- PMID: 34408013
- PMCID: PMC8428746
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100399
Fc Galactosylation Promotes Hexamerization of Human IgG1, Leading to Enhanced Classical Complement Activation
Abstract
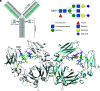
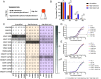
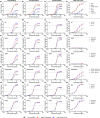
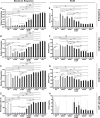
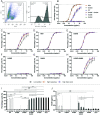
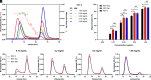
Human IgG contains one evolutionarily conserved N-linked glycan in its Fc region at position 297. This glycan is crucial for Fc-mediated functions, including its induction of the classical complement cascade. This is induced after target recognition through the IgG-Fab regions, allowing neighboring IgG-Fc tails to associate through Fc:Fc interaction, ultimately leading to hexamer formation. This hexamerization seems crucial for IgG to enable efficient interaction with the globular heads of the first complement component C1q and subsequent complement activation. In this study, we show that galactose incorporated in the IgG1-Fc enhances C1q binding, C4, C3 deposition, and complement-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in human erythrocytes and Raji cells. IgG1-Fc sialylation slightly enhanced binding of C1q, but had little effect on downstream complement activation. Using various mutations that decrease or increase hexamerization capacity of IgG1, we show that IgG1-Fc galactosylation has no intrinsic effect on C1q binding to IgG1, but enhances IgG1 hexamerization potential and, thereby, complement activation. These data suggest that the therapeutic potential of Abs can be amplified without introducing immunogenic mutations, by relatively simple glycoengineering.
Copyright © 2021 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential of Murine IgG1 and Human IgG4 to Inhibit the Classical Complement and Fcγ Receptor Activation Pathways.Front Immunol. 2018 May 9;9:958. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00958. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29867943 Free PMC article.
-
Fc galactosylation follows consecutive reaction kinetics and enhances immunoglobulin G hexamerization for complement activation.MAbs. 2021 Jan-Dec;13(1):1893427. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2021.1893427. MAbs. 2021. PMID: 33682619 Free PMC article.
-
Fc-Galactosylation of Human Immunoglobulin Gamma Isotypes Improves C1q Binding and Enhances Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity.Front Immunol. 2017 Jun 6;8:646. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00646. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28634480 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Concepts of Altered Immunoglobulin G Galactosylation in Autoimmune Diseases.Front Immunol. 2018 Mar 19;9:553. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00553. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29616041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modular organization of proteins containing C1q-like globular domain.Immunopharmacology. 1999 May;42(1-3):15-21. doi: 10.1016/s0162-3109(99)00011-9. Immunopharmacology. 1999. PMID: 10408361 Review.
Cited by
-
IgG subclass and Fc glycosylation shifts are linked to the transition from pre- to inflammatory autoimmune conditions.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 3;13:1006939. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1006939. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36405742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BNT162b2-induced neutralizing and non-neutralizing antibody functions against SARS-CoV-2 diminish with age.Cell Rep. 2022 Oct 25;41(4):111544. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111544. Epub 2022 Oct 5. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 36252569 Free PMC article.
-
High-Throughput Glycomic Methods.Chem Rev. 2022 Oct 26;122(20):15865-15913. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c01031. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Chem Rev. 2022. PMID: 35797639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Afucosylated IgG responses in humans - structural clues to the regulation of humoral immunity.Trends Immunol. 2022 Oct;43(10):800-814. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2022.08.001. Epub 2022 Aug 22. Trends Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36008258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Opportunities in Glycan Engineering for Therapeutic Proteins.Antibodies (Basel). 2022 Jan 10;11(1):5. doi: 10.3390/antib11010005. Antibodies (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35076453 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kapur R., Della Valle L., Verhagen O. J. H. M., Hipgrave Ederveen A., Ligthart P., de Haas M., Kumpel B., Wuhrer M., van der Schoot C. E., Vidarsson G.. 2015. Prophylactic anti-D preparations display variable decreases in Fc-fucosylation of anti-D. Transfusion 55: 553–562. - PubMed
-
- Sonneveld M. E., Natunen S., Sainio S., Koeleman C. A. M., Holst S., Dekkers G., Koelewijn J., Partanen J., van der Schoot C. E., Wuhrer M., Vidarsson G.. 2016. Glycosylation pattern of anti-platelet IgG is stable during pregnancy and predicts clinical outcome in alloimmune thrombocytopenia. Br. J. Haematol. 174: 310–320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

