Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein in Cancer and Diabetes
- PMID: 34384271
- PMCID: PMC9125520
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2021.0038
Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein in Cancer and Diabetes
Abstract
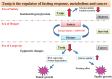
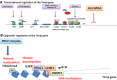
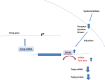
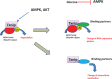
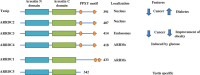
Significance: Thioredoxin-interacting protein (Txnip) is an α-arrestin protein that acts as a cancer suppressor. Txnip is simultaneously a critical regulator of energy metabolism. Other alpha-arrestin proteins also play key roles in cell biology and cancer. Recent Advances: Txnip expression is regulated by multilayered mechanisms, including transcriptional regulation, microRNA, messenger RNA (mRNA) stabilization, and protein degradation. The Txnip-based connection between cancer and metabolism has been widely recognized. Meanwhile, new aspects are proposed for the mechanism of action of Txnip, including the regulation of RNA expression and autophagy. Arrestin domain containing 3 (ARRDC3), another α-arrestin protein, regulates endocytosis and signaling, whereas ARRDC1 and ARRDC4 regulate extracellular vesicle formation. Critical Issues: The mechanism of action of Txnip is yet to be elucidated. The regulation of intracellular protein trafficking by arrestin family proteins has opened an emerging field of biology and medical research, which needs to be examined further. Future Directions: A fundamental understanding of the mechanism of action of Txnip and other arrestin family members needs to be explored in the future to combat diseases such as cancer and diabetes. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 36, 1001-1022.
Keywords: ARRDC3; RNA; TBP-2); autophagy; cancer; thioredoxin; thioredoxin-binding protein-2; thioredoxin-interacting protein (Txnip; α-arrestin.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thioredoxin-independent regulation of metabolism by the alpha-arrestin proteins.J Biol Chem. 2009 Sep 11;284(37):24996-5003. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.018093. Epub 2009 Jul 15. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19605364 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological and Pathophysiological Roles of Thioredoxin Interacting Protein: A Perspective on Redox Inflammation and Metabolism.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023 Feb;38(4-6):442-460. doi: 10.1089/ars.2022.0022. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023. PMID: 35754346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure of the N-terminal domain of human thioredoxin-interacting protein.Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013 Mar;69(Pt 3):333-44. doi: 10.1107/S0907444912047099. Epub 2013 Feb 16. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2013. PMID: 23519408
-
Thioredoxin interacting protein: redox dependent and independent regulatory mechanisms.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012 Mar 15;16(6):587-96. doi: 10.1089/ars.2011.4137. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012. PMID: 21929372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thioredoxin-interacting protein is a biomechanical regulator of Src activity: key role in endothelial cell stress fiber formation.Circ Res. 2014 Mar 28;114(7):1125-32. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.301315. Epub 2014 Feb 10. Circ Res. 2014. PMID: 24515523 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Additive and Interactive Genetically Contextual Effects of HbA1c on cg19693031 Methylation in Type 2 Diabetes.Genes (Basel). 2022 Apr 13;13(4):683. doi: 10.3390/genes13040683. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35456489 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis-based advanced therapies as treatment approaches for metabolic and cardiovascular diseases.Cell Death Differ. 2024 Sep;31(9):1104-1112. doi: 10.1038/s41418-024-01350-1. Epub 2024 Jul 27. Cell Death Differ. 2024. PMID: 39068204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
METTL14 drives growth and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by regulating pri-miR-93-5p maturation and TXNIP expression.Genes Genomics. 2024 Feb;46(2):213-229. doi: 10.1007/s13258-023-01436-z. Epub 2023 Aug 18. Genes Genomics. 2024. PMID: 37594665
-
A Toxoplasma gondii thioredoxin with cell adhesion and antioxidant function.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Aug 15;14:1404120. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1404120. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39211799 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA STARD7-AS1 suppresses cervical cancer cell proliferation while promoting autophagy by regulating miR-31-5p/TXNIP axis to inactivate the mTOR signaling.J Gynecol Oncol. 2024 Jul;35(4):e97. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2024.35.e97. Epub 2024 Apr 19. J Gynecol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38670562 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ago T, Liu T, Zhai P, Chen W, Li H, Molkentin JD, Vatner SF, and Sadoshima J. A redox-dependent pathway for regulating class II HDACs and cardiac hypertrophy. Cell 133: 978–993, 2008. - PubMed
-
- Ahsan MK, Masutani H, Yamaguchi Y, Kim YC, Nosaka K, Matsuoka M, Nishinaka Y, Maeda M, and Yodoi J. Loss of interleukin-2-dependency in HTLV-I-infected T cells on gene silencing of thioredoxin-binding protein-2. Oncogene 25: 2181–2191, 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

