Inflammation and Alzheimer's Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications by Natural Products
- PMID: 34381308
- PMCID: PMC8352708
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/9982954
Inflammation and Alzheimer's Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications by Natural Products
Abstract
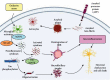
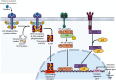
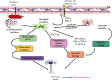
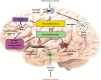
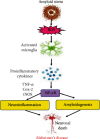
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder with no clear causative event making the disease difficult to diagnose and treat. The pathological hallmarks of AD include amyloid plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, and widespread neuronal loss. Amyloid-beta has been extensively studied and targeted to develop an effective disease-modifying therapy, but the success rate in clinical practice is minimal. Recently, neuroinflammation has been focused on as the event in AD progression to be targeted for therapies. Various mechanistic pathways including cytokines and chemokines, complement system, oxidative stress, and cyclooxygenase pathways are linked to neuroinflammation in the AD brain. Many cells including microglia, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes work together to protect the brain from injury. This review is focused to better understand the AD inflammatory and immunoregulatory processes to develop novel anti-inflammatory drugs to slow down the progression of AD.
Copyright © 2021 Mashoque Ahmad Rather et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting Inflammatory Pathways in Alzheimer's Disease: A Focus on Natural Products and Phytomedicines.CNS Drugs. 2019 May;33(5):457-480. doi: 10.1007/s40263-019-00619-1. CNS Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30900203 Review.
-
LRP1 knockdown aggravates Aβ1-42-stimulated microglial and astrocytic neuroinflammatory responses by modulating TLR4/NF-κB/MAPKs signaling pathways.Exp Cell Res. 2020 Sep 15;394(2):112166. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112166. Epub 2020 Jul 6. Exp Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32645395
-
IKK2/NF-κB Activation in Astrocytes Reduces amyloid β Deposition: A Process Associated with Specific Microglia Polarization.Cells. 2021 Oct 6;10(10):2669. doi: 10.3390/cells10102669. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685649 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of LRP1 Exacerbates Inflammatory Response Via TLR4/NF-κB/MAPKs Signaling Pathways in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice.Mol Neurobiol. 2020 Sep;57(9):3727-3743. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-01982-7. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2020. PMID: 32572761
-
Inhibitors of NF-κB and P2X7/NLRP3/Caspase 1 pathway in microglia: Novel therapeutic opportunities in neuroinflammation induced early-stage Alzheimer's disease.J Neuroimmunol. 2019 Jan 15;326:62-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2018.11.010. Epub 2018 Nov 20. J Neuroimmunol. 2019. PMID: 30502599 Review.
Cited by
-
Dopamine Activates the D1R-Zn2+ Signaling Pathway to Trigger Inflammatory Response in Primary-Cultured Rat Embryonic Cortical Neurons.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Oct;43(7):3593-3604. doi: 10.1007/s10571-023-01367-z. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37289255
-
Apelin-13 Improves Cognitive Impairment and Repairs Hippocampal Neuronal Damage by Activating PGC-1α/PPARγ Signaling.Neurochem Res. 2023 May;48(5):1504-1515. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03844-1. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Neurochem Res. 2023. PMID: 36512295
-
Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in Alzheimer's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 25;19(6):e0305322. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305322. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38917167 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Effects of N-methyl-(2S, 4R)-trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline (NMP) against Amyloid-β-Induced Alzheimer's Disease Mouse Model.Nutrients. 2023 Dec 1;15(23):4986. doi: 10.3390/nu15234986. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 38068844 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of amyloid-β-mimicking peptide hydrogel matrix on neuronal progenitor cell phenotype.Acta Biomater. 2024 Jul 15;183:89-100. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.05.020. Epub 2024 May 25. Acta Biomater. 2024. PMID: 38801867
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

