Picroside II Improves Severe Acute Pancreatitis-Induced Hepatocellular Injury in Rats by Affecting JAK2/STAT3 Phosphorylation Signaling
- PMID: 34368363
- PMCID: PMC8337114
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/9945149
Picroside II Improves Severe Acute Pancreatitis-Induced Hepatocellular Injury in Rats by Affecting JAK2/STAT3 Phosphorylation Signaling
Abstract
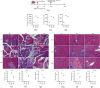
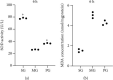
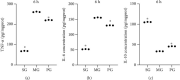
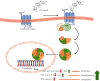
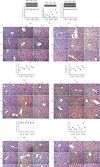
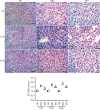
Picroside II is an important ingredient agent in Traditional Chinese medicine and hoped to reduce hepatocellular injury caused by severe acute pancreatitis (SAP). An SAP-induced hepatocellular injury model was established in rats by using pentobarbital sodium. 27 rats were divided into 3 groups: the sham group (SG), model group (MG), and Picroside groups (PG). SAP-induced hepatocellular injury was assessed using hematoxylin and eosin staining. We measured hepatocellular enzymes (amylase (AMY), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and aspartate aminotransferase (AST)), oxidative stress factors (superoxidase dismutase (SOD) and malondialdehyde (MDA)), and inflammatory factors (tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), interleukin- (IL-) 6, and IL-10), apoptotic factors (BAX and cleaved caspase 3), and inflammatory signaling (Janus kinase 2 (JAK2)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), p-JAK2, and p-STAT3) in hepatocellular tissues. The SAP-induced hepatocellular injury model was successfully established. Picroside II treatment repaired hepatocellular injury by reducing the activities of AMY, ALT, and AST; reducing the levels of MDA, TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, p-JAK2, p-STAT3, BAX, and cleaved caspase 3; and increasing the levels of SOD and IL-10. Picroside II exerted protective function for the SAP-induced hepatocellular injury model. Picroside II improved SAP-induced hepatocellular injury and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties by affecting JAK2/STAT3 phosphorylation signaling.
Copyright © 2021 Xuehua Piao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Picroside II Improves Severe Acute Pancreatitis-Induced Intestinal Barrier Injury by Inactivating Oxidative and Inflammatory TLR4-Dependent PI3K/AKT/NF-κB Signaling and Improving Gut Microbiota.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Apr 12;2020:3589497. doi: 10.1155/2020/3589497. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32351672 Free PMC article.
-
Da-Huang-Fu-Zi-Tang attenuates liver injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Dec 12;150(3):960-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.09.051. Epub 2013 Oct 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24161994
-
Effect of SOCS3 on lung injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis through regulating JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Nov;23(22):10123-10131. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201911_19582. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31799684
-
Picroside II Shows Protective Functions for Severe Acute Pancreatitis in Rats by Preventing NF-κB-Dependent Autophagy.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:7085709. doi: 10.1155/2017/7085709. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 28713490 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of Alprostadil on Acute Pancreatitis in Rats via Inhibiting Janus Kinase 2 (JAK2)/STAT3 Signal Transduction Pathway.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Oct 13;25:7694-7701. doi: 10.12659/MSM.919148. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31606729 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Milk fat globule epidermal growth factor 8 alleviates liver injury in severe acute pancreatitis by restoring autophagy flux and inhibiting ferroptosis in hepatocytes.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Feb 21;30(7):728-741. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i7.728. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38515944 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

