Developing-country vaccine manufacturers' technical capabilities can make a difference in global immunization
- PMID: 34362602
- PMCID: PMC8330991
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.07.044
Developing-country vaccine manufacturers' technical capabilities can make a difference in global immunization
Abstract
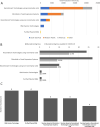
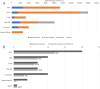
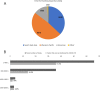
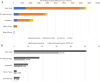
Members of the Developing Countries Vaccine Manufacturers' Network (DCVMN) have been actively engaged in the development of COVID-19 vaccine candidates. According to the WHO COVID-19 vaccine landscape updated on 29 December 2020, 18 member manufacturers had vaccines in preclinical or clinical trials, including three members with candidates in Phase III trials. Once successful candidates have been identified there will be a need for large scale vaccine manufacturing and supply, in which DCVMN member manufacturers can play a key role. In an internal survey in 2019, DCVMN members reported the capability to supply over 3.5 billion vaccine doses annually, and the provision of over 50 distinct vaccines to 170 countries. To describe the capabilities of DCVMN member manufacturers more precisely, a 121-question survey was circulated to 41 Network members. The survey assessed the manufacturers' capabilities in utilizing various technology platforms, cell cultures and filling technologies, in addition to their capacities for manufacturing drug products. The survey also evaluated manufacturers' preparedness to dedicate existing capacities to COVID-19 vaccine production. Results revealed that sampled manufacturers have strong capabilities for manufacturing vaccines based on recombinant technologies, particularly with mammalian cells, and microbial and yeast expression systems. Capabilities in utilizing cell cultures were distributed across multiple cell types, however manufacturing capacities with Vero and CHO cells were prominent. Formulating and filling findings illustrated further large-scale capabilities of Network members. Sampled manufacturers reported that over 50% of their capacity for vaccine manufacturing could be dedicated to COVID-19 vaccine production.
Keywords: COVID-19 vaccines; Global supply; Manufacturing capabilities; Public health; Technology platforms.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
COVID-19 vaccine capacity: Challenges and mitigation - The DCVMN perspective.Vaccine. 2021 Aug 16;39(35):4932-4937. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.07.007. Epub 2021 Jul 13. Vaccine. 2021. PMID: 34325932 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging manufacturers engagements in the COVID -19 vaccine research, development and supply.Vaccine. 2020 Jul 22;38(34):5418-5423. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.06.022. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Vaccine. 2020. PMID: 32600908 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccines for a healthy future: 21st DCVMN Annual General Meeting 2020 report.Vaccine. 2021 Apr 28;39(18):2479-2488. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.03.025. Epub 2021 Apr 7. Vaccine. 2021. PMID: 33838948 Free PMC article.
-
The Developing Countries Vaccine Manufacturers' Network (DCVMN) is a critical constituency to ensure access to vaccines in developing countries.Vaccine. 2008 Mar 20;26(13):1611-5. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.01.034. Epub 2008 Feb 6. Vaccine. 2008. PMID: 18294742 Review.
-
The Future of Epidemic and Pandemic Vaccines to Serve Global Public Health Needs.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Mar 17;11(3):690. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11030690. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36992275 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Standardization and Key Aspects of the Development of Whole Yeast Cell Vaccines.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 14;14(12):2792. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122792. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36559285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contrasting academic approaches to COVID-19 vaccine production and distribution: What can the Oxford and Texas experiences teach us about pandemic response?Health Aff Sch. 2024 Jan 31;2(2):qxae012. doi: 10.1093/haschl/qxae012. eCollection 2024 Feb. Health Aff Sch. 2024. PMID: 38756554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020. Available at https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re.... [Accessed 8th January 2021].
-
- COVID-19 Corona virus Pandemic cases, Worldometer. Available at https://www.worldometers.info/coronavirus/ [Accessed 2nd January 2021]
-
- BBC News. Coronavirus: WHO warns of ‘no silver bullet’ amid vaccine search. News article. 3rd August 2020. Available at https://www.bbc.com/news/world-53643455 [Accessed 8th January 2021]
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

