Emerging liver organoid platforms and technologies
- PMID: 34341842
- PMCID: PMC8329140
- DOI: 10.1186/s13619-021-00089-1
Emerging liver organoid platforms and technologies
Abstract
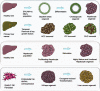
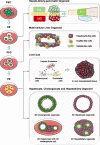
Building human organs in a dish has been a long term goal of researchers in pursue of physiologically relevant models of human disease and for replacement of worn out and diseased organs. The liver has been an organ of interest for its central role in regulating body homeostasis as well as drug metabolism. An accurate liver replica should contain the multiple cell types found in the organ and these cells should be spatially organized to resemble tissue structures. More importantly, the in vitro model should recapitulate cellular and tissue level functions. Progress in cell culture techniques and bioengineering approaches have greatly accelerated the development of advance 3-dimensional (3D) cellular models commonly referred to as liver organoids. These 3D models described range from single to multiple cell type containing cultures with diverse applications from establishing patient-specific liver cells to modeling of chronic liver diseases and regenerative therapy. Each organoid platform is advantageous for specific applications and presents its own limitations. This review aims to provide a comprehensive summary of major liver organoid platforms and technologies developed for diverse applications.
Keywords: Disease models; Liver; Organoids; Regenerative therapy; Stem cells.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A decade of liver organoids: Advances in disease modeling.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023 Jul;29(3):643-669. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2022.0428. Epub 2023 Mar 6. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36880210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioengineering Liver Organoids for Diseases Modelling and Transplantation.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Dec 13;9(12):796. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9120796. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges for the Applications of Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Liver Organoids.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 1;9:748576. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.748576. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34660606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomaterials and bioengineering to guide tissue morphogenesis in epithelial organoids.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Nov 17;10:1038277. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1038277. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36466337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancement of Organoid Technology in Regenerative Medicine.Regen Eng Transl Med. 2023;9(1):83-96. doi: 10.1007/s40883-022-00271-0. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Regen Eng Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 35968268 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A decade of liver organoids: Advances in disease modeling.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023 Jul;29(3):643-669. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2022.0428. Epub 2023 Mar 6. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36880210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Crosstalk between Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells and Hepatocytes in Homeostasis and under Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 16;24(20):15212. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015212. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modeling Liver Development and Disease in a Dish.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 2;24(21):15921. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115921. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modelling metabolic diseases and drug response using stem cells and organoids.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2022 Dec;18(12):744-759. doi: 10.1038/s41574-022-00733-z. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 36071283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived planar neural organoids assembled on synthetic hydrogels.J Tissue Eng. 2024 Feb 14;15:20417314241230633. doi: 10.1177/20417314241230633. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. J Tissue Eng. 2024. PMID: 38361535 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achberger K, Probst C, Haderspeck J, Bolz S, Rogal J, Chuchuy J, Nikolova M, Cora V, Antkowiak L, Haq W, Shen N, Schenke-Layland K, Ueffing M, Liebau S, Loskill P. Merging organoid and organ-on-a-chip technology to generate complex multi-layer tissue models in a human retina-on-a-chip platform. eLife. 2019;8:e46188. doi: 10.7554/eLife.46188. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akbari S, Sevinç GG, Ersoy N, Basak O, Kaplan K, Sevinç K, Ozel E, Sengun B, Enustun E, Ozcimen B, Bagriyanik A, Arslan N, Önder TT, Erdal E. Robust, Long-term culture of endoderm-derived hepatic organoids for disease modeling. Stem Cell Rep. 2019;13(4):627–641. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2019.08.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Almeda-Valdés P, Aguilar-Olivos NE, Uribe M, Méndez-Sánchez N. Chapter 25 - the metabolic syndrome, oxidative stress, and the liver. In: Muriel P, editor. Liver pathophysiology. Boston: Academic; 2017. pp. 323–329.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
