Impact of age-related T cell dynamics on the identification of biomarkers predictive of immunotherapy discontinuation: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 34337428
- PMCID: PMC8323507
- DOI: 10.1002/aac2.12012
Impact of age-related T cell dynamics on the identification of biomarkers predictive of immunotherapy discontinuation: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: The impact of biologic aging on immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) toxicity and efficacy is underexplored in metastatic melanoma (MM). In peripheral blood T-lymphocytes (PBTLs), biologic aging is characterized by changes in T-cell composition and cellular senescence. Whether indicators of PBTL biologic aging vary in MM patients or can be used to predict premature ICI discontinuation (pID) is unknown.
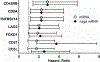
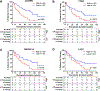
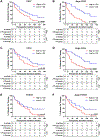
Methods: We prospectively collected PBTLs from 117 cancer-free controls and 46 MM patients scheduled to begin pembrolizumab or nivolumab monotherapy. 74 mRNAs indicative of T-cell subsets, activation, co-stimuation/inhibition and cellular senescence were measured by Nanostring. Relationships between each mRNA and chronologic age were assessed in patients and controls. Candidate biomarkers were identified by calculating the hazard ratio (HR) for pID in patients divided into low and high groups based on log-transformed mRNA levels or the magnitude by which each mRNA measurement deviated from the control trend (Δage). Area under the curve (AUC) analyses explored the ability of each biomarker to discriminate between patients with and without pID at 6 months and 1 year.
Results: Fifteen mRNAs correlated with chronologic age in controls, including markers of T-cell subsets, differentiation, cytokine production and co-stimulation/inhibition. None of these mRNAs remained correlated with age in patients. Median follow-up was 94.8 (1.6-195.7) weeks and 35 of 46 patients discontinued therapy (23 progression, 7 toxicity, 5 comorbidity/patient preference). Elevated pre-therapy CD8A (HR 2.2[1.1-4.9]), CD45RB (HR 2.9[1.4-5.8]) and TNFRSF14 (HR 2.2[1.1-4.5]) levels predicted pID independent of Δage-correction. CD3ε, CD27 and FOXO1 predicted pID only after Δage-correction (HR 2.5[1.3-5.1]; 3.7[1.8-7.8]; 2.1[1.1-4.3]). AUC analysis identified Δage-CD3ε and -CD27 as candidate predictors of pID (AUC=0.73; 0.75).
Conclusions: Correlations between transcriptional markers of PBTL composition and chronologic age are disrupted in MM. Correcting for normal, age-related trends in biomarker expression unveils new biomarker candidates predictive of ICI outcomes.
Keywords: Aging biomarker; CD27; T cell; aging; anti-PD-1; biomarker; checkpoint inhibitor; melanoma; senescence.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest. Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Association of Epigenetic Age and p16INK4a With Markers of T-Cell Composition in a Healthy Cohort.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2020 Nov 13;75(12):2299-2303. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glaa108. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32361724 Free PMC article.
-
Biologic subtypes of melanoma predict survival benefit of combination anti-PD1+anti-CTLA4 immune checkpoint inhibitors versus anti-PD1 monotherapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Jan;9(1):e001642. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001642. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33483342 Free PMC article.
-
Closed system RT-qPCR as a potential companion diagnostic test for immunotherapy outcome in metastatic melanoma.J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Sep 18;7(1):254. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0731-9. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31533832 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers for Clinical Benefit of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment-A Review From the Melanoma Perspective and Beyond.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 28;9:1474. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01474. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30002656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
First-line Immunotherapy-based Combinations for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis.Eur Urol Oncol. 2021 Oct;4(5):755-765. doi: 10.1016/j.euo.2021.03.001. Epub 2021 Mar 20. Eur Urol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33757737 Review.
Cited by
-
Peripheral blood CD3+ T-cell gene expression biomarkers correlate with clinical frailty in patients with haematological malignancies.Br J Haematol. 2022 Oct;199(1):100-105. doi: 10.1111/bjh.18336. Epub 2022 Jun 29. Br J Haematol. 2022. PMID: 35766906 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Franklin C, Livingstone E, Roesch A, Schilling B, Schadendorf D. Immunotherapy in melanoma: Recent advances and future directions. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2017;43(3):604–611. - PubMed
-
- Teng F, Meng X, Kong L, Yu J. Progress and challenges of predictive biomarkers of anti PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy: A systematic review. Cancer Lett. 2018;414:166–173. - PubMed
-
- Nikolich-Zugich J The twilight of immunity: emerging concepts in aging of the immune system. Nat Immunol. 2018;19(1):10–19. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
