Cf-02, a novel benzamide-linked small molecule, blunts NF-κB activation and NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and improves acute onset of accelerated and severe lupus nephritis in mice
- PMID: 34314075
- PMCID: PMC10083056
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.202100047R
Cf-02, a novel benzamide-linked small molecule, blunts NF-κB activation and NLRP3 inflammasome assembly and improves acute onset of accelerated and severe lupus nephritis in mice
Abstract
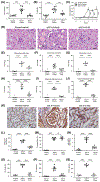
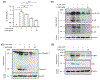
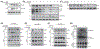
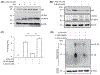
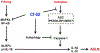
In the present study, acute onset of severe lupus nephritis was successfully treated in mice using a new, benzamide-linked, small molecule that targets immune modulation and the NLRP3 inflammasome. Specifically, 6-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-3-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-2H-benzo[e][1,3]oxazine-2,4(3H)-dione (Cf-02) (a) reduced serum levels of IgG anti-dsDNA, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, (b) inhibited activation of dendritic cells and differentially regulated T cell functions, and (c) suppressed the NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome axis, targeting priming and activating signals of the inflammasome. Moreover, treatment with Cf-02 significantly inhibited secretion of IL-1β in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages, but this effect was abolished by autophagy induction. These results recommend Cf-02 as a promising drug candidate for the serious renal conditions associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Future investigations should examine whether Cf-02 may also be therapeutic in other types of chronic kidney disease involving NLRP3 inflammasome-driven signaling.
Keywords: NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome axis; autophagy; benzamide-linked small molecule; severe lupus nephritis.
© 2021 Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Each author of this work declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
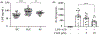


Similar articles
-
Accelerated, severe lupus nephritis benefits from treatment with honokiol by immunoregulation and differentially regulating NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome and sirtuin 1/autophagy axis.FASEB J. 2020 Oct;34(10):13284-13299. doi: 10.1096/fj.202001326R. Epub 2020 Aug 19. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32813287
-
Icariin alleviates murine lupus nephritis via inhibiting NF-κB activation pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome.Life Sci. 2018 Sep 1;208:26-32. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.07.009. Epub 2018 Jul 6. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 30146016
-
Role of vitamin D/VDR nuclear translocation in down-regulation of NF-κB/NLRP3/caspase-1 axis in lupus nephritis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Nov;100:108131. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108131. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34536747
-
Bay11-7082 attenuates murine lupus nephritis via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-κB activation.Int Immunopharmacol. 2013 Sep;17(1):116-22. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.05.027. Epub 2013 Jun 12. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23770281
-
Tris DBA Ameliorates Accelerated and Severe Lupus Nephritis in Mice by Activating Regulatory T Cells and Autophagy and Inhibiting the NLRP3 Inflammasome.J Immunol. 2020 Mar 15;204(6):1448-1461. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1801610. Epub 2020 Feb 14. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32060137
Cited by
-
Multi-Omics Identification of Genetic Alterations in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Therapeutic Efficacy of HNC018 as a Novel Multi-Target Agent for c-MET/STAT3/AKT Signaling Axis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 16;24(12):10247. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210247. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373393 Free PMC article.
-
NLRP3 Inflammasome: Checkpoint Connecting Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Autoimmune Diseases.Front Immunol. 2021 Oct 11;12:732933. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.732933. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34707607 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tam LS, Li EK, Lai FM, Chan YK, Szeto CC. Mesangial lupus nephritis in Chinese is associated with a high rate of transformation to higher grade nephritis. Lupus. 2003;12:665–671. - PubMed
-
- Weening JJ, D’Agati VD, Schwartz MM, et al. The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. Kidney Int. 2004;65:521–530. - PubMed
-
- Whittall-Garcia LP, Torres-Ruiz J, Zentella-Dehesa A, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps are a source of extracellular HMGB1 in lupus nephritis: associations with clinical and histopathological features. Lupus. 2019;28:1549–1557. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

