Tuning Beforehand: A Foresight on RNA Interference (RNAi) and In Vitro-Derived dsRNAs to Enhance Crop Resilience to Biotic and Abiotic Stresses
- PMID: 34299307
- PMCID: PMC8306419
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22147687
Tuning Beforehand: A Foresight on RNA Interference (RNAi) and In Vitro-Derived dsRNAs to Enhance Crop Resilience to Biotic and Abiotic Stresses
Abstract
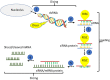
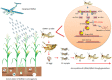
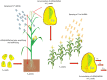
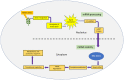
Crop yield is severely affected by biotic and abiotic stresses. Plants adapt to these stresses mainly through gene expression reprogramming at the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. Recently, the exogenous application of double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) and RNA interference (RNAi) technology has emerged as a sustainable and publicly acceptable alternative to genetic transformation, hence, small RNAs (micro-RNAs and small interfering RNAs) have an important role in combating biotic and abiotic stresses in plants. RNAi limits the transcript level by either suppressing transcription (transcriptional gene silencing) or activating sequence-specific RNA degradation (post-transcriptional gene silencing). Using RNAi tools and their respective targets in abiotic stress responses in many crops is well documented. Many miRNAs families are reported in plant tolerance response or adaptation to drought, salinity, and temperature stresses. In biotic stress, the spray-induced gene silencing (SIGS) provides an intelligent method of using dsRNA as a trigger to silence target genes in pests and pathogens without producing side effects such as those caused by chemical pesticides. In this review, we focus on the potential of SIGS as the most recent application of RNAi in agriculture and point out the trends, challenges, and risks of production technologies. Additionally, we provide insights into the potential applications of exogenous RNAi against biotic stresses. We also review the current status of RNAi/miRNA tools and their respective targets on abiotic stress and the most common responsive miRNA families triggered by stress conditions in different crop species.
Keywords: RNAi; drought; dsRNA; environmental risks; gene silencing; heat; insects; miRNA; risk; salinity; siRNA; spray-induced gene silencing (SIGS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biotic stress triggered small RNA and RNAi defense response in plants.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Jul;47(7):5511-5522. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05583-4. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32562176 Review.
-
Recent trends and advances of RNA interference (RNAi) to improve agricultural crops and enhance their resilience to biotic and abiotic stresses.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2023 Jan;194:600-618. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.11.035. Epub 2022 Dec 10. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36529010 Review.
-
Role of microRNAs in biotic and abiotic stress responses in crop plants.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014 Sep;174(1):93-115. doi: 10.1007/s12010-014-0914-2. Epub 2014 May 29. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 24869742 Review.
-
RNA Interference (RNAi) Induced Gene Silencing: A Promising Approach of Hi-Tech Plant Breeding.Int J Biol Sci. 2014 Oct 11;10(10):1150-8. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.10452. eCollection 2014. Int J Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25332689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNAi as a Foliar Spray: Efficiency and Challenges to Field Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 14;23(12):6639. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126639. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743077 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cross-Kingdom RNA Transport Based on Extracellular Vesicles Provides Innovative Tools for Plant Protection.Plants (Basel). 2024 Sep 27;13(19):2712. doi: 10.3390/plants13192712. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomaterials coupled with microRNAs for alleviating plant stress: a new opening towards sustainable agriculture.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2022 Apr;28(4):791-818. doi: 10.1007/s12298-022-01163-x. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2022. PMID: 35592477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quantification of DNA Methylation by ELISA in Epigenetic Studies in Plant Tissue Culture: A Theoretical-Practical Guide.Methods Mol Biol. 2024;2827:323-350. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3954-2_22. Methods Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38985280
-
Effects of differentially expressed microRNAs induced by rootstocks and silicon on improving chilling tolerance of cucumber seedlings (Cucumis sativus L.).BMC Genomics. 2023 May 10;24(1):250. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09337-x. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37165319 Free PMC article.
-
Plants' Response Mechanisms to Salinity Stress.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jun 8;12(12):2253. doi: 10.3390/plants12122253. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375879 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abhary M., Rezk A. RNAi Technology: APotential Tool in Plant Breeding. In: Al-Khayri J.M., Jain S.M., Johnson D.V., editors. Advances in Plant Breeding Strategies: Biotechnology and Molecular Tools. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2016. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

