Epigenetic regulation of energy metabolism in obesity
- PMID: 34289049
- PMCID: PMC8530523
- DOI: 10.1093/jmcb/mjab043
Epigenetic regulation of energy metabolism in obesity
Abstract
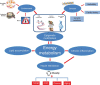
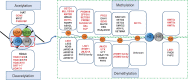
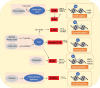
Obesity has reached epidemic proportions globally. Although modern adoption of a sedentary lifestyle coupled with energy-dense nutrition is considered to be the main cause of obesity epidemic, genetic preposition contributes significantly to the imbalanced energy metabolism in obesity. However, the variants of genetic loci identified from large-scale genetic studies do not appear to fully explain the rapid increase in obesity epidemic in the last four to five decades. Recent advancements of next-generation sequencing technologies and studies of tissue-specific effects of epigenetic factors in metabolic organs have significantly advanced our understanding of epigenetic regulation of energy metabolism in obesity. The epigenome, including DNA methylation, histone modifications, and RNA-mediated processes, is characterized as mitotically or meiotically heritable changes in gene function without alteration of DNA sequence. Importantly, epigenetic modifications are reversible. Therefore, comprehensively understanding the landscape of epigenetic regulation of energy metabolism could unravel novel molecular targets for obesity treatment. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge on the roles of DNA methylation, histone modifications such as methylation and acetylation, and RNA-mediated processes in regulating energy metabolism. We also discuss the effects of lifestyle modifications and therapeutic agents on epigenetic regulation of energy metabolism in obesity.
Keywords: energy metabolism; epigenetics; obesity; treatment.
© The Author(s) (2021). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, CEMCS, CAS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An Overview of Epigenetics in Obesity: The Role of Lifestyle and Therapeutic Interventions.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 25;23(3):1341. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031341. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenomics in stress tolerance of plants under the climate change.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Jul;50(7):6201-6216. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08539-6. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37294468 Review.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Adipokines.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Aug 10;18(8):1740. doi: 10.3390/ijms18081740. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28796178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rewriting cellular fate: epigenetic interventions in obesity and cellular programming.Mol Med. 2024 Oct 10;30(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00944-2. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39390356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Targets and their Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy.Curr Top Med Chem. 2018;18(28):2395-2419. doi: 10.2174/1568026619666181224095449. Curr Top Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 30582481 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated genetic and epigenetic analyses uncovered GLP1R association with metabolically healthy obesity.Int J Obes (Lond). 2024 Mar;48(3):324-329. doi: 10.1038/s41366-023-01414-1. Epub 2023 Nov 17. Int J Obes (Lond). 2024. PMID: 37978261
-
Epigenetics in obesity: Mechanisms and advances in therapies based on natural products.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2024 Feb;12(1):e1171. doi: 10.1002/prp2.1171. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2024. PMID: 38293783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Obesity: causes, consequences, treatments, and challenges.J Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Oct 21;13(7):463-465. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjab056. J Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34673982 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Editorial: Metabolism and Epigenetics.Front Genet. 2022 Mar 10;13:877538. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.877538. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35360874 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus subset stimulates tissue thermogenesis via preoptic area outputs.Mol Metab. 2024 Jun;84:101951. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2024.101951. Epub 2024 May 8. Mol Metab. 2024. PMID: 38729241 Free PMC article.

