Identification of Novel miRNAs and Their Target Genes in the Response to Abscisic Acid in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 34281207
- PMCID: PMC8268864
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22137153
Identification of Novel miRNAs and Their Target Genes in the Response to Abscisic Acid in Arabidopsis
Abstract
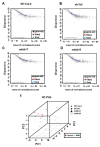
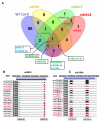
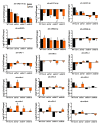
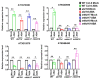
miRNAs are involved in various biological processes, including adaptive responses to abiotic stress. To understand the role of miRNAs in the response to ABA, ABA-responsive miRNAs were identified by small RNA sequencing in wild-type Arabidopsis, as well as in abi1td, mkkk17, and mkkk18 mutants. We identified 10 novel miRNAs in WT after ABA treatment, while in abi1td, mkkk17, and mkkk18 mutants, three, seven, and nine known miRNAs, respectively, were differentially expressed after ABA treatment. One novel miRNA (miRn-8) was differentially expressed in the mkkk17 mutant. Potential target genes of the miRNA panel were identified using psRNATarget. Sequencing results were validated by quantitative RT-PCR of several known and novel miRNAs in all genotypes. Of the predicted targets of novel miRNAs, seven target genes of six novel miRNAs were further validated by 5' RLM-RACE. Gene ontology analyses showed the potential target genes of ABA-responsive known and novel miRNAs to be involved in diverse cellular processes in plants, including development and stomatal movement. These outcomes suggest that a number of the identified miRNAs have crucial roles in plant responses to environmental stress, as well as in plant development, and might have common regulatory roles in the core ABA signaling pathway.
Keywords: ABI1 PP2C; Arabidopsis thaliana; MAPKKK17; MAPKKK18; abscisic acid; miRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest is declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genomic profiling of exogenous abscisic acid-responsive microRNAs in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum).BMC Genomics. 2016 Jun 3;17:423. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-2591-8. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27260799 Free PMC article.
-
Functional analyses of the ABI1-related protein phosphatase type 2C reveal evolutionarily conserved regulation of abscisic acid signaling between Arabidopsis and the moss Physcomitrella patens.Plant Mol Biol. 2009 Jun;70(3):327-40. doi: 10.1007/s11103-009-9476-z. Epub 2009 Mar 6. Plant Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19266168
-
Gene expression profiling of ozone-treated Arabidopsis abi1td insertional mutant: protein phosphatase 2C ABI1 modulates biosynthesis ratio of ABA and ethylene.Planta. 2009 Oct;230(5):1003-17. doi: 10.1007/s00425-009-1001-8. Epub 2009 Aug 25. Planta. 2009. PMID: 19705149
-
Regulation of Arabidopsis MAPKKK18 by ABI1 and SnRK2, components of the ABA signaling pathway.Plant Signal Behav. 2016;11(4):e1139277. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2016.1139277. Plant Signal Behav. 2016. PMID: 26852793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Updates on the Role of ABSCISIC ACID INSENSITIVE 5 (ABI5) and ABSCISIC ACID-RESPONSIVE ELEMENT BINDING FACTORs (ABFs) in ABA Signaling in Different Developmental Stages in Plants.Cells. 2021 Aug 5;10(8):1996. doi: 10.3390/cells10081996. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440762 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differences in the intraspecies copy number variation of Arabidopsis thaliana conserved and nonconserved miRNA genes.Funct Integr Genomics. 2023 Apr 10;23(2):120. doi: 10.1007/s10142-023-01043-x. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37036577 Free PMC article.
-
The Bro1-like domain-containing protein, AtBro1, modulates growth and abiotic stress responses in Arabidopsis.Front Plant Sci. 2023 May 12;14:1157435. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1157435. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37251780 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of miRNAs and their target genes associated with improved maize seed vigor induced by gibberellin.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Sep 13;13:1008872. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1008872. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36176685 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Exogenous dsRNA on miRNA Composition in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plants (Basel). 2024 Aug 22;13(16):2335. doi: 10.3390/plants13162335. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204771 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification of the CBF Gene Family and ICE Transcription Factors in Walnuts and Expression Profiles under Cold Conditions.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 19;25(1):25. doi: 10.3390/ijms25010025. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38203199 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Danquah A., De Zélicourt A., Boudsocq M., Neubauer J., Frei Dit Frey N., Leonhardt N., Pateyron S., Gwinner F., Tamby J.P., Ortiz-Masia D., et al. Identification and characterization of an ABA-activated MAP kinase cascade in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2015;82:232–244. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12808. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mitula F., Tajdel M., Cieśla A., Kasprowicz-Maluśki A., Kulik A., Babula-Skowrońska D., Michalak M., Dobrowolska G., Sadowski J., Ludwików A., et al. Arabidopsis ABA-Activated Kinase MAPKKK18 is Regulated by Protein Phosphatase 2C ABI1 and the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015;56:2351–2367. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcv146. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

