Nanomaterials for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Head and Neck Cancers: A Review
- PMID: 34279276
- PMCID: PMC8269895
- DOI: 10.3390/ma14133706
Nanomaterials for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Head and Neck Cancers: A Review
Abstract
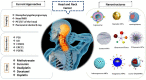
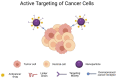
Head and neck cancer (HNC) is a category of cancers that typically arise from the nose-, mouth-, and throat-lining squamous cells. The later stage of HNC diagnosis significantly affects the patient's survival rate. This makes it mandatory to diagnose this cancer with a suitable biomarker and imaging techniques at the earlier stages of growth. There are limitations to traditional technologies for early detection of HNC. Furthermore, the use of nanocarriers for delivering chemo-, radio-, and phototherapeutic drugs represents a promising approach for improving the outcome of HNC treatments. Several studies with nanostructures focus on the development of a targeted and sustained release of anticancer molecules with reduced side effects. Besides, nanovehicles could allow co-delivering of anticancer drugs for synergistic activity to counteract chemo- or radioresistance. Additionally, a new generation of smart nanomaterials with stimuli-responsive properties have been developed to distinguish between unique tumor conditions and healthy tissue. In this light, the present article reviews the mechanisms used by different nanostructures (metallic and metal oxide nanoparticles, polymeric nanoparticles, quantum dots, liposomes, nanomicelles, etc.) to improve cancer diagnosis and treatment, provides an up-to-date picture of the state of the art in this field, and highlights the major challenges for future improvements.
Keywords: biomaterials; cancer treatment; nanomaterials; nanoparticles; stimuli-responsive materials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Stimuli-responsive drug delivery systems for head and neck cancer therapy.Drug Deliv. 2021 Dec;28(1):272-284. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2021.1876182. Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 33501883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevention of microbial biofilms - the contribution of micro and nanostructured materials.Curr Med Chem. 2014;21(29):3311. doi: 10.2174/0929867321666140304101314. Curr Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24606506
-
Stimuli-responsive Polymeric Nanosystems for Therapeutic Applications.Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(11):910-921. doi: 10.2174/1381612827666211208150210. Curr Pharm Des. 2022. PMID: 34879797 Review.
-
Smart nanomaterials for cancer diagnosis and treatment.Nano Converg. 2022 May 15;9(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s40580-022-00313-x. Nano Converg. 2022. PMID: 35569081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle-Mediated Combination Therapy: Two-in-One Approach for Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 20;19(10):3264. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103264. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30347840 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Magnetic Nanoparticles Used in Oncology.Materials (Basel). 2021 Oct 10;14(20):5948. doi: 10.3390/ma14205948. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34683540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Insights and Progress in the Clinical Management of Head and Neck Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Dec 10;14(24):6079. doi: 10.3390/cancers14246079. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanotheranostics-based Management of Head and Neck Cancer.Nanotheranostics. 2023 Feb 5;7(2):202-209. doi: 10.7150/ntno.81724. eCollection 2023. Nanotheranostics. 2023. PMID: 36793352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The current status of nanotechnological approaches to therapy and drug delivery in otolaryngology: A contemporary review.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2022 Oct 20;7(6):1762-1772. doi: 10.1002/lio2.952. eCollection 2022 Dec. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 36544970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in head and neck surgical oncology.J Surg Oncol. 2024 Jan;129(1):32-39. doi: 10.1002/jso.27529. Epub 2023 Nov 22. J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 37990842 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fiuza-Luces C., Santos-Lozano A., Joyner M., Carrera-Bastos P., Picazo O., Zugaza J.L., Izquierdo M., Ruilope L.M., Lucia A. Exercise benefits in cardiovascular disease: Beyond attenuation of traditional risk factors. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018;15:731–743. doi: 10.1038/s41569-018-0065-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Olshan A.F. Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Prevention of Head and Neck Cancer. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2010. pp. 1–21. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

