Diagnostic Accuracy of Dried Blood Spots Collected on HemaSpot HF Devices Compared to Venous Blood Specimens To Estimate Measles and Rubella Seroprevalence
- PMID: 34259557
- PMCID: PMC8386429
- DOI: 10.1128/mSphere.01330-20
Diagnostic Accuracy of Dried Blood Spots Collected on HemaSpot HF Devices Compared to Venous Blood Specimens To Estimate Measles and Rubella Seroprevalence
Abstract
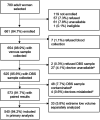
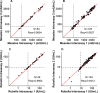
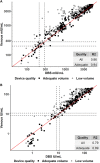
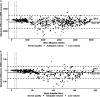
Fingerprick blood spotted onto filter paper offers an alternative to venous blood for use in population-based surveillance because it is comparatively inexpensive, acceptable, and easy to manage in the field. Prior studies have shown excellent agreement for immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody detection from dried blood spots (DBS) and venous blood samples. However, much of this evidence is from high-income settings or laboratories where the samples were unlikely to be exposed to extreme temperatures and humidity, factors known to degrade DBS. We report the diagnostic accuracy of DBS collected using HemaSpot HF devices against venous sera in measuring measles- and rubella-specific IgG antibodies in a household serosurvey conducted in two districts in India. Paired serum and DBS samples collected by fingerprick were collected from women aged 15 to 50 years enrolled in a serosurvey in Palghar District of Maharashtra and Kanpur Nagar District of Uttar Pradesh in India. Specimen quality and volume were assessed in the laboratory. Samples were tested for antimeasles and antirubella IgG antibodies by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (Euroimmun). Sensitivity of antibody detection by DBS was greater than 98%, and specificity was 90% and 98%, for measles and rubella IgG, respectively. Antibody concentrations were strongly correlated between paired specimens with adequate volume (measles R2 = 0.94; rubella R2 = 0.89). Although correlation was poor if DBS specimens had lower volumes, impact on qualitative results was minimal. This study showed DBS collected with HemaSpot HF devices can generate highly accurate results of measles- and rubella-specific IgG compared to sera in community-based surveys when protocols are optimized for DBS specimens. IMPORTANCE Dried blood spot (DBS) collection provides an easy, practical, and acceptable alternative to venous blood collection, especially for community-based studies, provided that results from DBS are accurate. We demonstrated high sensitivity and specificity for measles- and rubella-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) with DBS collected via HemaSpot HF devices compared to serum samples. This is one of the largest community-based diagnostic accuracy studies of measles and rubella antibody testing with DBS and the first application we are aware of using HemaSpot HF device for measles and rubella serology. Results support the use of DBS in community-based serosurveillance.
Keywords: ELISA; India; diagnostic accuracy; dried blood spots; measles; rubella; serology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optimization and Stability Testing of Four Commercially Available Dried Blood Spot Devices for Estimating Measles and Rubella IgG Antibodies.mSphere. 2021 Aug 25;6(4):e0049021. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00490-21. Epub 2021 Jul 14. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34259563 Free PMC article.
-
Use of a commercial ELISA for the detection of measles-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) in dried blood spots collected from children living in low-resource settings.J Med Virol. 2015 Sep;87(9):1491-9. doi: 10.1002/jmv.24136. Epub 2015 May 18. J Med Virol. 2015. PMID: 25988945
-
Dried blood spots versus sera for detection of rubella virus-specific immunoglobulin M (IgM) and IgG in samples collected during a rubella outbreak in Peru.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007 Nov;14(11):1522-5. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00144-07. Epub 2007 Sep 19. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17881506 Free PMC article.
-
A review of testing used in seroprevalence studies on measles and rubella.Vaccine. 2016 Jul 29;34(35):4119-4122. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.06.006. Epub 2016 Jun 20. Vaccine. 2016. PMID: 27340096 Review.
-
Diagnostic accuracy of serological diagnosis of hepatitis C and B using dried blood spot samples (DBS): two systematic reviews and meta-analyses.BMC Infect Dis. 2017 Nov 1;17(Suppl 1):700. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2777-y. BMC Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 29143672 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence in a Berlin Kindergarten Environment: A Cross-Sectional Study, September 2021.Children (Basel). 2024 Mar 28;11(4):405. doi: 10.3390/children11040405. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38671622 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of the Analytes Applied in Genotypic HIV Drug Resistance Testing.Pathogens. 2022 Jun 29;11(7):739. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11070739. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35889985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimization and Stability Testing of Four Commercially Available Dried Blood Spot Devices for Estimating Measles and Rubella IgG Antibodies.mSphere. 2021 Aug 25;6(4):e0049021. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00490-21. Epub 2021 Jul 14. mSphere. 2021. PMID: 34259563 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2008. Recommendations from an ad hoc Meeting of the WHO Measles and Rubella Laboratory Network (LabNet) on use of alternative diagnostic samples for measles and rubella surveillance. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 57:657–660. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

