Primed to die: an investigation of the genetic mechanisms underlying noise-induced hearing loss and cochlear damage in homozygous Foxo3-knockout mice
- PMID: 34234110
- PMCID: PMC8263610
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-021-03972-6
Primed to die: an investigation of the genetic mechanisms underlying noise-induced hearing loss and cochlear damage in homozygous Foxo3-knockout mice
Abstract
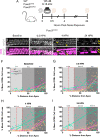
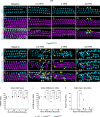
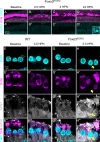
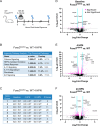
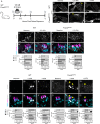
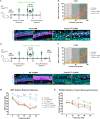
The prevalence of noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) continues to increase, with limited therapies available for individuals with cochlear damage. We have previously established that the transcription factor FOXO3 is necessary to preserve outer hair cells (OHCs) and hearing thresholds up to two weeks following mild noise exposure in mice. The mechanisms by which FOXO3 preserves cochlear cells and function are unknown. In this study, we analyzed the immediate effects of mild noise exposure on wild-type, Foxo3 heterozygous (Foxo3+/-), and Foxo3 knock-out (Foxo3-/-) mice to better understand FOXO3's role(s) in the mammalian cochlea. We used confocal and multiphoton microscopy to examine well-characterized components of noise-induced damage including calcium regulators, oxidative stress, necrosis, and caspase-dependent and caspase-independent apoptosis. Lower immunoreactivity of the calcium buffer Oncomodulin in Foxo3-/- OHCs correlated with cell loss beginning 4 h post-noise exposure. Using immunohistochemistry, we identified parthanatos as the cell death pathway for OHCs. Oxidative stress response pathways were not significantly altered in FOXO3's absence. We used RNA sequencing to identify and RT-qPCR to confirm differentially expressed genes. We further investigated a gene downregulated in the unexposed Foxo3-/- mice that may contribute to OHC noise susceptibility. Glycerophosphodiester phosphodiesterase domain containing 3 (GDPD3), a possible endogenous source of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), has not previously been described in the cochlea. As LPA reduces OHC loss after severe noise exposure, we treated noise-exposed Foxo3-/- mice with exogenous LPA. LPA treatment delayed immediate damage to OHCs but was insufficient to ultimately prevent their death or prevent hearing loss. These results suggest that FOXO3 acts prior to acoustic insult to maintain cochlear resilience, possibly through sustaining endogenous LPA levels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Noise-induced cochlear F-actin depolymerization is mediated via ROCK2/p-ERM signaling.J Neurochem. 2015 Jun;133(5):617-28. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13061. Epub 2015 Mar 2. J Neurochem. 2015. PMID: 25683353 Free PMC article.
-
Severe hearing loss and outer hair cell death in homozygous Foxo3 knockout mice after moderate noise exposure.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 21;7(1):1054. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01142-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28432353 Free PMC article.
-
Prestin regulation and function in residual outer hair cells after noise-induced hearing loss.PLoS One. 2013 Dec 20;8(12):e82602. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0082602. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24376553 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Oxidative Stress in Sensorineural Hearing Loss.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 9;25(8):4146. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084146. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of noise-induced hearing loss indicate multiple methods of prevention.Hear Res. 2007 Apr;226(1-2):22-43. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2006.10.006. Epub 2006 Dec 4. Hear Res. 2007. PMID: 17141991 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An update on Glycerophosphodiester Phosphodiesterases; From Bacteria to Human.Protein J. 2024 Apr;43(2):187-199. doi: 10.1007/s10930-024-10190-4. Epub 2024 Mar 16. Protein J. 2024. PMID: 38491249 Review.
-
Increased central auditory gain in 5xFAD Alzheimer's disease mice as an early biomarker candidate for Alzheimer's disease diagnosis.Front Neurosci. 2023 May 26;17:1106570. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1106570. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37304021 Free PMC article.
-
GDE7 produces cyclic phosphatidic acid in the ER lumen functioning as a lysophospholipid mediator.Commun Biol. 2023 May 16;6(1):524. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-04900-4. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37193762 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Lysophospholipid Metabolism in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Stem Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 8;13(14):3434. doi: 10.3390/cancers13143434. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34298649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overcoming barriers: a review on innovations in drug delivery to the middle and inner ear.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 19;14:1207141. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1207141. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37927600 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- White PM. Genetic susceptibility to hearing loss from noise exposure. Hear J. 2019;72:8–9. doi: 10.1097/01.HJ.0000602896.08600.65. - DOI
-
- Deng A, Ma L, Zhou X, Wang X, Wang S, Chen X. FoxO3 transcription factor promotes autophagy after oxidative stress injury in HT22 cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2020;99:1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

