Clinical Efficacy of Temozolomide and Its Predictors in Aggressive Pituitary Tumors and Pituitary Carcinomas: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34220696
- PMCID: PMC8250148
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.700007
Clinical Efficacy of Temozolomide and Its Predictors in Aggressive Pituitary Tumors and Pituitary Carcinomas: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
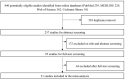
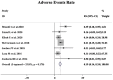
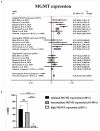
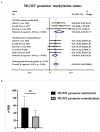
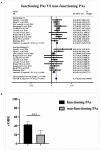
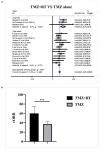
Background: A growing number of evidences suggest that TMZ applications can generate impressive benefits for APT and PC patients. However, the definite role of TMZ for individuals remains unclarified due to the variation between studies. And the predictive factors to alter its efficacy remain debatable. Objective: To evaluate the long-term effectiveness and safety profile of TMZ in the treatment of pituitary malignancies, and delineate the predictors during its clinical employment. Results: A literature retrieval was conducted from online databases for studies published up to December 31, 2020. Twenty one studies involving 429 patients were identified. TMZ exhibited 41% radiological overall response rate (rORR). The biochemical response rate was determinate in 53% of the functioning subset. Two-year and 4-year survival rate were 79 and 61%, respectively. TMZ prolonged the median PFS and OS as 20.18 and 40.24 months. TMZ-related adverse events occurred in 19% of patients. Regarding predictors of TMZ response, rORR was dramatically improved in patients with low/intermediate MGMT expression than those with high-MGMT (>50%) (p < 0.001). The benefit of TMZ varied according to functioning subtype of patients, with greater antitumor activities in functioning subgroups and fewer activities in non-functioning sets (p < 0.001). Notably, the concomitant therapy of radiotherapy and TMZ significantly increased the rORR (p = 0.007). Conclusion: TMZ elicits clinical benefits with moderate adverse events in APT and PC patients. MGMT expression and clinical subtype of secreting function might be vital predictors of TMZ efficacy. In the future, the combination of radiotherapy with TMZ may further improve the clinical outcomes than TMZ monotherapy.
Keywords: aggressive pituitary tumors; meta-analysis; pituitary adenoma; pituitary carcinomas; temozolomide.
Copyright © 2021 Luo, Tan, Chen, Hu, Wang, Zhu, Jiao, Duan, Zhu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Temozolomide in aggressive pituitary tumours and pituitary carcinomas.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Dec;36(6):101713. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2022.101713. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 36274026 Review.
-
Efficacy of Temozolomide Therapy in Patients With Aggressive Pituitary Adenomas and Carcinomas-A German Survey.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Mar 1;105(3):dgz211. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgz211. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 31746334
-
The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of carmustine implants and temozolomide for the treatment of newly diagnosed high-grade glioma: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Nov;11(45):iii-iv, ix-221. doi: 10.3310/hta11450. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17999840 Review.
-
Long-term therapy with temozolomide is a feasible option for newly diagnosed glioblastoma: a single-institution experience with as many as 101 temozolomide cycles.Neurosurg Focus. 2014 Dec;37(6):E4. doi: 10.3171/2014.9.FOCUS14502. Neurosurg Focus. 2014. PMID: 25434389
-
Long-term outcome and MGMT as a predictive marker in 24 patients with atypical pituitary adenomas and pituitary carcinomas given treatment with temozolomide.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Apr;100(4):1689-98. doi: 10.1210/jc.2014-4350. Epub 2015 Feb 3. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 25646794
Cited by
-
Aggressive and Metastatic Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumors: Therapeutic Management and Off-Label Drug Use.J Clin Med. 2023 Dec 25;13(1):116. doi: 10.3390/jcm13010116. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38202123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prolactin-secreting pituitary adenomas: male-specific differences in pathogenesis, clinical presentation and treatment.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 2;15:1338345. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1338345. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38370355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of a Novel SSTR3 Full Agonist for the Treatment of Nonfunctioning Pituitary Adenomas.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 30;15(13):3453. doi: 10.3390/cancers15133453. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444563 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in understanding and managing pituitary adenomas.Fac Rev. 2023 Mar 21;12:6. doi: 10.12703/r/12-6. eCollection 2023. Fac Rev. 2023. PMID: 36968144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Convolutional Neural Network Model for Detecting Sellar Floor Destruction of Pituitary Adenoma on Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scans.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jul 4;16:900519. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.900519. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35860294 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

