Optimization of Novel Naproxen-Loaded Chitosan/Carrageenan Nanocarrier-Based Gel for Topical Delivery: Ex Vivo, Histopathological, and In Vivo Evaluation
- PMID: 34207951
- PMCID: PMC8230576
- DOI: 10.3390/ph14060557
Optimization of Novel Naproxen-Loaded Chitosan/Carrageenan Nanocarrier-Based Gel for Topical Delivery: Ex Vivo, Histopathological, and In Vivo Evaluation
Abstract
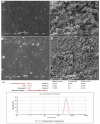
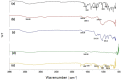
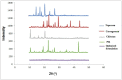
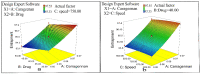
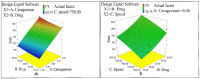
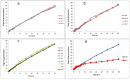
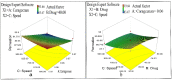
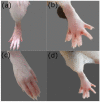
Naproxen (NAP) is commonly used for pain, inflammation, and stiffness associated with arthritis. However, systemic administration is linked with several gastrointestinal tract (GIT) side effects. The present work aims to prepare and evaluate NAP nanoparticulate shells of chitosan (CS) and carrageenan (CRG) loaded into a Carbopol 940 (Ca-940) gel system with unique features of sustained drug delivery as well as improved permeation through a topical route. Moreover, this study aims to evaluate its ex vivo, histopathological, and in vivo anti-inflammatory activity in albino Wistar rats. The percentage of ex vivo drug permeation patterns in the optimized formulation (No) was higher (88.66%) than the control gel (36.195%). Oral toxicity studies of developed nanoparticles in albino rabbits showed that the NAP-loaded CS/CRG are non-toxic and, upon histopathological evaluation, no sign of incompatibility was observed compared to the control group. A In Vivo study showed that the optimized gel formulation (No) was more effective than the control gel (Nc) in treating arthritis-associated inflammation. The sustained permeation and the absence of skin irritation make this novel NAP nanoparticle-loaded gel based on CS/CRG a suitable drug delivery system for topical application and has the potential for improved patient compliance and reduced GIT-related side effects in arthritis.
Keywords: Ca-940 gel; anti-inflammatory; carrageenan; chitosan; nanocarriers; naproxen; polyelectrolyte complexation; toxicity study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy of Dapoxetine HCl by Nano-Vesicle Transdermal Gel for Treatment of Carrageenan-Induced Rat Paw Edema.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2020 Apr 14;21(3):113. doi: 10.1208/s12249-020-01656-6. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2020. PMID: 32291553
-
Evaluation of glycofurol-based gel as a new vehicle for topical application of naproxen.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2010 Sep;11(3):1138-46. doi: 10.1208/s12249-010-9485-x. Epub 2010 Jul 23. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2010. PMID: 20652458 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro, Ex Vivo, and In Vivo Evaluation of Nanoparticle-Based Topical Formulation Against Candida albicans Infection.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 8;13:909851. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.909851. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35873577 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of Nanoethosomal Transgel of Naproxen Sodium for the Treatment of Arthritis.Curr Drug Deliv. 2020;17(10):885-897. doi: 10.2174/1567201817666200724170203. Curr Drug Deliv. 2020. PMID: 32713340
-
Development and Evaluation of Naproxen Sodium Gel Using Piper cubeba for Enhanced Transdermal Drug Delivery and Therapeutic Facilitation.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2017;11(1):28-35. doi: 10.2174/1872211311666170105114459. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2017. PMID: 28056749
Cited by
-
Solubilization and Controlled Release Strategy of Poorly Water-Soluble Drugs.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Nov 2;15(11):1353. doi: 10.3390/ph15111353. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36355525 Free PMC article.
-
Transdermal Microneedle-Mediated Delivery of Rasagiline Nanoparticles.Arch Razi Inst. 2023 Jun 30;78(3):1017-1022. doi: 10.22092/ARI.2022.360192.2562. eCollection 2023 Jun. Arch Razi Inst. 2023. PMID: 38028835 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction in Pathogenic Biofilms by the Photoactive Composite of Bacterial Cellulose and Nanochitosan Dots under Blue and Green Light.J Funct Biomater. 2024 Mar 14;15(3):72. doi: 10.3390/jfb15030072. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 38535265 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing lornoxicam-loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) and (polyethylene glycol) nanoparticles for transdermal delivery: ex vivo/in vivo inflammation evaluation.Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024 Jul 2;19(16):1471-1485. doi: 10.1080/17435889.2024.2359356. Epub 2024 Jul 2. Nanomedicine (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38953843
-
Photo-Phytotherapeutic Gel Composed of Copaifera reticulata, Chlorophylls, and k-Carrageenan: A New Perspective for Topical Healing.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Nov 24;14(12):2580. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122580. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36559074 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lubberts E., van den Berg W.B. Madame Curie Bioscience Database. Landes Bioscience; Austin, TX, USA: 2013. Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Collagen-Induced Arthritis. - PubMed
-
- Micheli L., Bozdag M., Akgul O., Carta F., Guccione C., Bergonzi M.C., Bilia A.R., Cinci L., Lucarini E., Parisio C. Pain Relieving Effect of-NSAIDs-CAIs Hybrid Molecules: Systemic and Intra-Articular Treatments against Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019;20:1923. doi: 10.3390/ijms20081923. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Keyhanian F., Alizadeh N., Shojaie A. Spectrophotometric determination of Naproxen as ion-pair with bromophenol blue in bulk, pharmaceutical preparation and human serum samples. Curr. Chem. Lett. 2014;3:15–22. doi: 10.5267/j.ccl.2013.10.006. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

