Soluble Programmed Death Ligand-1 (sPD-L1): A Pool of Circulating Proteins Implicated in Health and Diseases
- PMID: 34204509
- PMCID: PMC8233757
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13123034
Soluble Programmed Death Ligand-1 (sPD-L1): A Pool of Circulating Proteins Implicated in Health and Diseases
Abstract
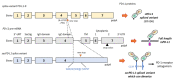
Upon T-cell receptor stimulation, the Programmed cell Death-1 receptor (PD-1) expressed on T-cells can interact with its ligand PD-L1 expressed at the surface of cancer cells or antigen-presenting cells. Monoclonal antibodies targeting PD-1 or PD-L1 are routinely used for the treatment of cancers, but their clinical efficacy varies largely across the variety of tumor types. A part of the variability is linked to the existence of several forms of PD-L1, either expressed on the plasma membrane (mPD-L1), at the surface of secreted cellular exosomes (exoPD-L1), in cell nuclei (nPD-L1), or as a circulating, soluble protein (sPD-L1). Here, we have reviewed the different origins and roles of sPD-L1 in humans to highlight the biochemical and functional heterogeneity of the soluble protein. sPD-L1 isoforms can be generated essentially by two non-exclusive processes: (i) proteolysis of m/exoPD-L1 by metalloproteases, such as metalloproteinases (MMP) and A disintegrin and metalloproteases (ADAM), which are capable of shedding membrane PD-L1 to release an active soluble form, and (ii) the alternative splicing of PD-L1 pre-mRNA, leading in some cases to the release of sPD-L1 protein isoforms lacking the transmembrane domain. The expression and secretion of sPD-L1 have been observed in a large variety of pathologies, well beyond cancer, notably in different pulmonary diseases, chronic inflammatory and autoimmune disorders, and viral diseases. The expression and role of sPD-L1 during pregnancy are also evoked. The structural heterogeneity of sPD-L1 proteins, and associated functional/cellular plurality, should be kept in mind when considering sPD-L1 as a biomarker or as a drug target. The membrane, exosomal and soluble forms of PD-L1 are all integral parts of the highly dynamic PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway, essential for immune-tolerance or immune-escape.
Keywords: PD-1/PD-L1; autoimmune diseases; cancer; immune checkpoint; immuno-suppression; protein maturation; soluble PD-L1.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest associated with this publication and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Biological Characteristics and Clinical Significance of Soluble PD-1/PD-L1 and Exosomal PD-L1 in Cancer.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 21;13:827921. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.827921. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35386715 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of sPD-1 and sPD-Ls in the pathogenesis of connective tissue disease.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 Mar 28;48(3):444-454. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2023.220263. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37164928 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Soluble PD-L1 as a Biomarker in Malignant Melanoma Treated with Checkpoint Blockade.Cancer Immunol Res. 2017 Jun;5(6):480-492. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-16-0329. Epub 2017 May 18. Cancer Immunol Res. 2017. PMID: 28522460 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Soluble PD-L1: a potential dynamic predictive biomarker for immunotherapy in patients with proficient mismatch repair colorectal cancer.J Transl Med. 2023 Jan 13;21(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-03879-0. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36639643 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble PD-L1 as a Prognostic Factor for Immunotherapy Treatment in Solid Tumors: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 21;23(22):14496. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214496. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430974 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of T cell evasion by Epstein-Barr virus and implications for tumor survival.Front Immunol. 2023 Dec 21;14:1289313. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1289313. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38179040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble programmed death ligand 1 as prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving nivolumab, pembrolizumab or atezolizumab therapy.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 18;14(1):8993. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59791-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38637655 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid subsets impede the efficacy of anti-PD1 therapy in patients with advanced gastric cancer (WJOG10417GTR study).J Immunother Cancer. 2024 Nov 3;12(11):e010174. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-010174. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39489543 Free PMC article.
-
Membranes on the move: The functional role of the extracellular vesicle membrane for contact-dependent cellular signalling.J Extracell Vesicles. 2024 Apr;13(4):e12436. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12436. J Extracell Vesicles. 2024. PMID: 38649339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shedding Light on the Role of Exosomal PD-L1 (ExoPD-L1) in Cancer Progression: an Update.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Sep;82(3):1709-1720. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01340-7. Epub 2024 Jun 22. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38907940 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

