Role of Glucose-Lowering Medications in Erectile Dysfunction
- PMID: 34198786
- PMCID: PMC8201035
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm10112501
Role of Glucose-Lowering Medications in Erectile Dysfunction
Abstract
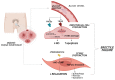
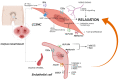
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a long-term complication of type 2 diabetes (T2D) widely known to affect the quality of life. Several aspects of altered metabolism in individuals with T2D may help to compromise the penile vasculature structure and functions, thus exacerbating the imbalance between smooth muscle contractility and relaxation. Among these, advanced glycation end-products and reactive oxygen species derived from a hyperglycaemic state are known to accelerate endothelial dysfunction by lowering nitric oxide bioavailability, the essential stimulus of relaxation. Although several studies have explained the pathogenetic mechanisms involved in the generation of erectile failure, few studies to date have described the efficacy of glucose-lowering medications in the restoration of normal sexual activity. Herein, we will present current knowledge about the main starters of the pathophysiology of diabetic ED and explore the role of different anti-diabetes therapies in the potential remission of ED, highlighting specific pathways whose activation or inhibition could be fundamental for sexual care in a diabetes setting.
Keywords: diabetes; erectile dysfunction; glucose-lowering medications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Implanted Muscle-Derived Stem Cells Ameliorate Erectile Dysfunction in a Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes, but Their Repair Capacity Is Impaired by Their Prior Exposure to the Diabetic Milieu.J Sex Med. 2016 May;13(5):786-97. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2016.02.168. J Sex Med. 2016. PMID: 27114192 Free PMC article.
-
AGE-breaker ALT-711 plus insulin could restore erectile function in streptozocin-induced type 1 diabetic rats.J Sex Med. 2014 Jun;11(6):1452-62. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12533. Epub 2014 Apr 28. J Sex Med. 2014. PMID: 24766706
-
Recent advances in the treatment of erectile dysfunction in patients with diabetes mellitus.Endocr Pract. 2003 Jan-Feb;9(1):52-63. doi: 10.4158/EP.9.1.52. Endocr Pract. 2003. PMID: 12917094 Review.
-
Advanced glycation end products in human penis: elevation in diabetic tissue, site of deposition, and possible effect through iNOS or eNOS.Urology. 1997 Dec;50(6):1016-26. doi: 10.1016/S0090-4295(97)00512-8. Urology. 1997. PMID: 9426743
-
Is Erectile Dysfunction an Example of Abnormal Endothelial Function?Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2016;14(2):163-7. doi: 10.2174/1570161114666151202205950. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26638795 Review.
Cited by
-
Erectile dysfunction and exosome therapy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 9;14:1123383. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1123383. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36967787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipose Tissue Dysfunction and Obesity-Related Male Hypogonadism.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 25;23(15):8194. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158194. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The corrective role of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for the genes controlling hypothalamus-pituitary-testis-axis in male obesity-associated secondary hypogonadism.Open Vet J. 2024 Jan;14(1):428-437. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2024.v14.i1.39. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Open Vet J. 2024. PMID: 38633156 Free PMC article.
-
Autologous Immune Cell-Based Regenerative Therapies to Treat Vasculogenic Erectile Dysfunction: Is the Immuno-Centric Revolution Ready for the Prime Time?Biomedicines. 2022 May 8;10(5):1091. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10051091. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35625828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Antihyperglycemic Drugs and Diet on Erectile Function: Results from a Perspective Study on a Population with Prediabetes and Diabetes.J Clin Med. 2022 Jun 13;11(12):3382. doi: 10.3390/jcm11123382. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35743453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Corona G., Giorda C.B., Cucinotta D., Guida P., Nada E., Aglialoro A., Albanese V., Albano S., Antonangelo C., Baccetti F., et al. Sexual dysfunction at the onset of type 2 diabetes: The interplay of depression, hormonal and cardiovascular factors. J. Sex. Med. 2014;11:2065–2073. doi: 10.1111/jsm.12601. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baena-Díez J.M., Peñafiel J., Subirana I., Ramos R., Elosua R., Marín-Ibañez A., Guembe M.J., Rigo F., Tormo-Díaz M.J., Moreno-Iribas C., et al. Risk of Cause-Specific Death in Individuals With Diabetes: A Competing Risks Analysis. Diabetes Care. 2016;39:1987–1995. doi: 10.2337/dc16-0614. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Corona G., Maseroli E., Rastrelli G., Francomano D., Aversa A., Hackett G.I., Ferri S., Sforza A., Maggi M. Is late-onset hypogonadotropic hypogonadism a specific age-dependent disease, or merely an epiphenomenon caused by accumulating disease-burden? Minerva Endocrinol. 2016;41:196–210. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

