Interleukin-35 is a critical regulator of immunity during helminth infections associated with multiple sclerosis
- PMID: 34197631
- PMCID: PMC8517594
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.13389
Interleukin-35 is a critical regulator of immunity during helminth infections associated with multiple sclerosis
Abstract
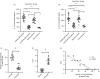
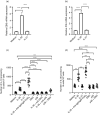
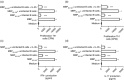
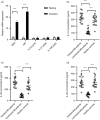
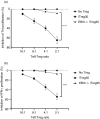
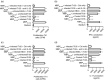
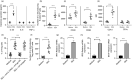
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is currently thought to arise by interactions between genetic susceptibility and environmental factors. Infections in general trigger autoimmune responses causing clinical manifestations of disease. However, as a result of regulatory T (Treg)- and regulatory B (Breg)-cell induction, helminth infections tend to dampen disease activity. IL-35, the newest member of the IL-12 family, is an inhibitory cytokine composed of an EBI3β chain subunit, and an IL-12p35 subunit. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of IL-35 during parasite infections occurring in individuals with MS. Numbers of IL-35-producing Breg cells are higher in CSF from helminth-infected than from uninfected MS subjects, a finding associated with decreased MRI disease activity. Interestingly, stimulation of CD19+ B cells with IL-35 promotes conversion of these cells to Breg cells producing both IL-35 and IL-10. Coculture of B cells from helminth-infected MS patients inhibits proliferation of Th1 and Th17 myelin peptide-specific T cells, as well as production of IFN-γ and IL-17. Following activation, CD4+ CD25+ Treg cells significantly upregulate expression of EBI3 and IL-12p35 mRNA. Furthermore, CD4+ CD25- T cells activated in the presence of IL-35 induce a population of cells with regulatory function, known as iTR35. Finally, B cells from normal individuals cultured in vitro in the presence of the helminth antigen SEA increase expression of the transcription BATF, IRF4 and IRF8, acquiring a pattern similar to that of IL-35 Breg cells. These data highlight the important immunoregulatory effects of IL-35 on both Breg and Treg cells, observed in helminth-infected MS subjects.
Keywords: EAE; IL-10; IL-35; helminths; multiple sclerosis; regulatory B cells; regulatory T cells.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests in reference to this manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Does helminth activation of toll-like receptors modulate immune response in multiple sclerosis patients?Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012 Aug 24;2:112. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00112. eCollection 2012. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22937527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory B cells, helminths, and multiple sclerosis.Methods Mol Biol. 2014;1190:257-69. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-1161-5_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 25015286
-
Immunomodulation of human CD19+CD25high regulatory B cells via Th17/Foxp3 regulatory T cells and Th1/Th2 cytokines.Hum Immunol. 2019 Oct;80(10):863-870. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2019.05.011. Epub 2019 Jun 28. Hum Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31262519
-
IL-12p35 induces expansion of IL-10 and IL-35-expressing regulatory B cells and ameliorates autoimmune disease.Nat Commun. 2017 Sep 28;8(1):719. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00838-4. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 28959012 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of CNS inflammatory demyelination.J Neurol Sci. 2013 Oct 15;333(1-2):76-87. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2013.03.002. Epub 2013 Apr 8. J Neurol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23578791 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of IL-35, as a Possible Biomarker for Follow-Up after Therapy, in Chronic Human Schistosoma Infection.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 May 17;11(5):995. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11050995. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37243099 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Definitive Regulatory B Cell Subsets by Cell Surface Phenotype, Function and Context.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 20;12:787464. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.787464. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34987513 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Ascaris infection is associated with higher frequencies of IL-10 producing B cells.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Sep 23;18(9):e0012520. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012520. eCollection 2024 Sep. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 39312581 Free PMC article.
-
The circulating IL-35+ regulatory B cells are associated with thyroid associated opthalmopathy.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 May;12(5):e1304. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1304. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 38804861 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-35 attenuates blood-brain barrier dysfunction caused by cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibiting brain endothelial cell injury.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Jul;10(14):776. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-2770. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35965799 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thompson AJ, Baranzini SE, Geurts J, Hemmer B, Ciccarelli O. Multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 2018;391:1622–36. - PubMed
-
- Ascherio A. Environmental factors in multiple sclerosis. Expert Rev Neurother. 2013;13(12 Suppl):3–9. - PubMed
-
- Correale J, Fiol M, Gilmore W. The risk of relapses in multiple sclerosis during systemic infections. Neurology. 2006;67:652–9. - PubMed
-
- Kivity S, Agmon‐Levin N, Blank M, Shoenfeld Y. Infections and autoimmunity–friends or foes? Trends Immunol. 2009;30:409–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

