Novel and atypical pathways for serotonin signaling
- PMID: 34195691
- PMCID: PMC8204760
- DOI: 10.12703/r/10-52
Novel and atypical pathways for serotonin signaling
Abstract
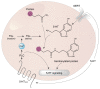
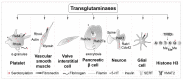
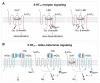
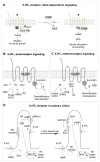
Serotonin (5-HT) appeared billions of years before 5-HT receptors and synapses. It is thus not surprising that 5-HT can control biological processes independently of its receptors. One example is serotonylation, which consists of covalent binding of 5-HT to the primary amine of glutamine. Over the past 20 years, serotonylation has been involved in the regulation of many signaling mechanisms. One of the most striking examples is the recent evidence that serotonylation of histone H3 constitutes an epigenetic mark. However, the pathophysiological role of histone H3 serotonylation remains to be discovered. All but one of the 5-HT receptors are G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). The signaling pathways they control are finely tuned, and new, unexpected regulatory mechanisms are being uncovered continuously. Some 5-HT receptors (5-HT2C, 5-HT4, 5-HT6, and 5-HT7) signal through mechanisms that require neither G-proteins nor β-arrestins, the two classical and almost universal GPCR signal transducers. 5-HT6 receptors are constitutively activated via their association with intracellular GPCR-interacting proteins (GIPs), including neurofibromin 1, cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5), and G-protein-regulated inducer of neurite outgrowth 1 (GPRIN1). Interactions of 5-HT6 receptor with Cdk5 and GPRIN1 are not concomitant but occur sequentially and play a key role in dendritic tree morphogenesis. Furthermore, 5-HT6 receptor-mediated G-protein signaling in neurons is different in the cell body and primary cilium, where it is modulated by smoothened receptor activation. Finally, 5-HT2A receptors form heteromers with mGlu2 metabotropic glutamate receptors. This heteromerization results in a specific phosphorylation of mGlu2 receptor on a serine residue (Ser843) upon agonist stimulation of 5-HT2A or mGlu2 receptor. mGlu2 receptor phosphorylation on Ser843 is an essential step in engagement of Gi/o signaling not only upon mGlu2 receptor activation but also following 5-HT2A receptor activation, and thus represents a key molecular event underlying functional crosstalk between both receptors.
Keywords: GPCR interacting protein; Serotonin; heteromerization; receptor; serotonylation.
Copyright: © 2021 Bockaert J et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
5-HT2A receptor-dependent phosphorylation of mGlu2 receptor at Serine 843 promotes mGlu2 receptor-operated Gi/o signaling.Mol Psychiatry. 2019 Nov;24(11):1610-1626. doi: 10.1038/s41380-018-0069-6. Epub 2018 Jun 1. Mol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 29858599
-
Role of interaction of mGlu2 and 5-HT2A receptors in antipsychotic effects.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2022 Nov;221:173474. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2022.173474. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2022. PMID: 36244526 Review.
-
Allosteric signaling through an mGlu2 and 5-HT2A heteromeric receptor complex and its potential contribution to schizophrenia.Sci Signal. 2016 Jan 12;9(410):ra5. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aab0467. Sci Signal. 2016. PMID: 26758213 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic interactions of the 5-HT6 receptor with protein partners control dendritic tree morphogenesis.Sci Signal. 2020 Feb 11;13(618):eaax9520. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aax9520. Sci Signal. 2020. PMID: 32047117
-
Serotonin 2A (5-HT2A) Receptor Function: Ligand-Dependent Mechanisms and Pathways.In: Chattopadhyay A, editor. Serotonin Receptors in Neurobiology. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2007. Chapter 6. In: Chattopadhyay A, editor. Serotonin Receptors in Neurobiology. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2007. Chapter 6. PMID: 21204452 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Allosteric Modulators of Serotonin Receptors: A Medicinal Chemistry Survey.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 28;17(6):695. doi: 10.3390/ph17060695. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38931362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin signalling in cancer: Emerging mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Jul;14(7):e1750. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1750. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38943041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implications of Transglutaminase-Mediated Protein Serotonylation in the Epigenetic Landscape, Small Cell Lung Cancer, and Beyond.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Feb 20;15(4):1332. doi: 10.3390/cancers15041332. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36831672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in Investigational Agents Targeting Serotonin-6 Receptors for the Treatment of Brain Disorders.Biomolecules. 2023 Feb 7;13(2):309. doi: 10.3390/biom13020309. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36830678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic and Molecular Response to High-Fat Diet Differs between Rats with Constitutionally High and Low Serotonin Tone.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 21;24(3):2169. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032169. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768493 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Azmitia E: Functional anatomy of the serotonergic system. In: Müller CaC, KA, editor. Handbook of Behavioral neurobiology of Serotonin. London: Academic Press, Elsevier; 2020. Reference Source
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
