DNA glycosylase deficiency leads to decreased severity of lupus in the Polb-Y265C mouse model
- PMID: 34186496
- PMCID: PMC8635285
- DOI: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2021.103152
DNA glycosylase deficiency leads to decreased severity of lupus in the Polb-Y265C mouse model
Abstract
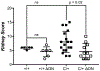
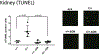
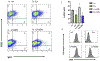
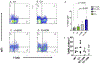
The Polb gene encodes DNA polymerase beta (Pol β), a DNA polymerase that functions in base excision repair (BER) and microhomology-mediated end-joining. The Pol β-Y265C protein exhibits low catalytic activity and fidelity, and is also deficient in microhomology-mediated end-joining. We have previously shown that the PolbY265C/+ and PolbY265C/C mice develop lupus. These mice exhibit high levels of antinuclear antibodies and severe glomerulonephritis. We also demonstrated that the low catalytic activity of the Pol β-Y265C protein resulted in accumulation of BER intermediates that lead to cell death. Debris released from dying cells in our mice could drive development of lupus. We hypothesized that deletion of the Neil1 and Ogg1 DNA glycosylases that act upstream of Pol β during BER would result in accumulation of fewer BER intermediates, resulting in less severe lupus. We found that high levels of antinuclear antibodies are present in the sera of PolbY265C/+ mice deleted of Ogg1 and Neil1 DNA glycosylases. However, these mice develop significantly less severe renal disease, most likely due to high levels of IgM in their sera.
Keywords: Base excision repair; DNA glycosylase; DNA polymerase beta; Oxidative DNA damage; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest
There are no competing interests.
Figures
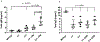
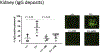
Similar articles
-
Mouse models to explore the biological and organismic role of DNA polymerase beta.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2024 Apr;65 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):57-71. doi: 10.1002/em.22593. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2024. PMID: 38619421 Review.
-
The hematopoietic compartment is sufficient for lupus development resulting from the POLB-Y265C mutation.PLoS One. 2022 Apr 29;17(4):e0267913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0267913. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35486639 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation of POLB causes lupus in mice.Cell Rep. 2014 Jan 16;6(1):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.12.017. Epub 2014 Jan 2. Cell Rep. 2014. PMID: 24388753 Free PMC article.
-
Base excision repair intermediates induce p53-independent cytotoxic and genotoxic responses.J Biol Chem. 2003 Oct 10;278(41):39951-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M306592200. Epub 2003 Jul 25. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12882965
-
Oxidative DNA damage in disease--insights gained from base excision repair glycosylase-deficient mouse models.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2014 Dec;55(9):689-703. doi: 10.1002/em.21886. Epub 2014 Jul 16. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2014. PMID: 25044514 Review.
Cited by
-
Mouse models to explore the biological and organismic role of DNA polymerase beta.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2024 Apr;65 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):57-71. doi: 10.1002/em.22593. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2024. PMID: 38619421 Review.
-
Levels of base excision repair proteins in CD4+ T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Dec 28;47(12):1655-1662. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2022.210485. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 36748375 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterisation of lupus low disease activity state (LLDAS) and DORIS remission by whole-blood transcriptome-based pathways in a pan-European systemic lupus erythematosus cohort.Ann Rheum Dis. 2024 Jun 12;83(7):889-900. doi: 10.1136/ard-2023-224795. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024. PMID: 38373843 Free PMC article.
-
Polβ/XRCC1 heterodimerization dictates DNA damage recognition and basal Polβ protein levels without interfering with mouse viability or fertility.DNA Repair (Amst). 2023 Mar;123:103452. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2023.103452. Epub 2023 Jan 20. DNA Repair (Amst). 2023. PMID: 36702010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Petri M (2008) Sex hormones and systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus, 17, 412–415. - PubMed
-
- Tedeschi SK, Bermas B and Costenbader KH (2013) Sexual disparities in the incidence and course of SLE and RA. Clin Immunol, 149, 211–218. - PubMed
-
- Alarcon-Segovia D, Alarcon-Riquelme ME, Cardiel MH, Caeiro F, Massardo L, Villa AR, Pons-Estel BA and Grupo Latinoamericano de Estudio del Lupus, E. (2005) Familial aggregation of systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and other autoimmune diseases in 1,177 lupus patients from the GLADEL cohort. Arthritis Rheum, 52, 1138–1147. - PubMed
-
- Deapen D, Escalante A, Weinrib L, Horwitz D, Bachman B, Roy-Burman P, Walker A and Mack TM (1992) A revised estimate of twin concordance in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum, 35, 311–318. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

