Unexpected Substituent Effects in Spiro-Compound Formation: Steering N-Aryl Propynamides and DMSO toward Site-Specific Sulfination in Quinolin-2-ones or Spiro[4,5]trienones
- PMID: 34184892
- PMCID: PMC8291627
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.1c00775
Unexpected Substituent Effects in Spiro-Compound Formation: Steering N-Aryl Propynamides and DMSO toward Site-Specific Sulfination in Quinolin-2-ones or Spiro[4,5]trienones
Abstract
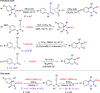
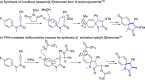
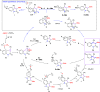
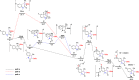
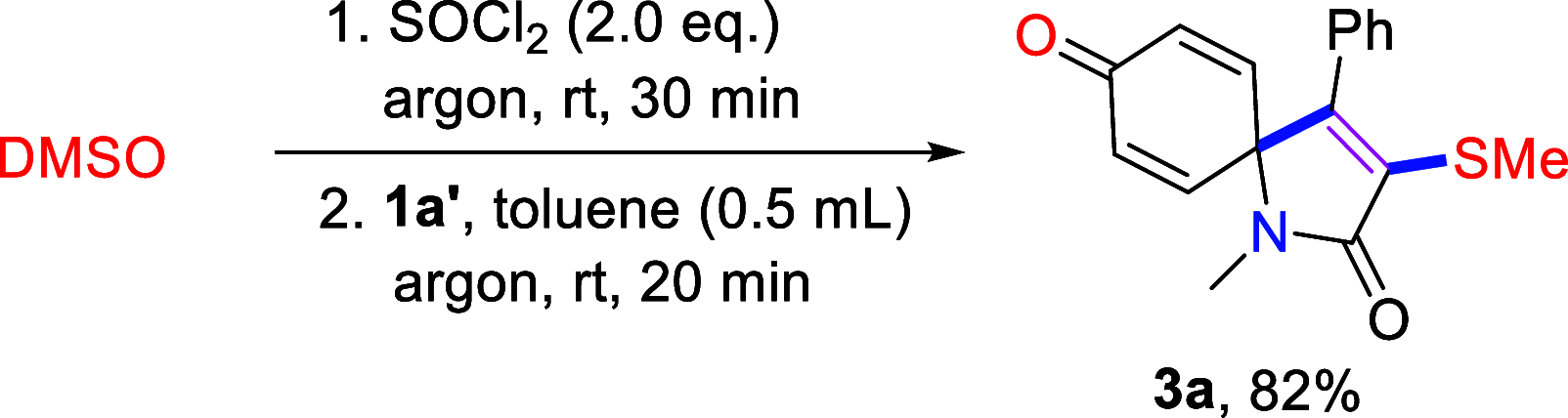
A highly substituent-dependent rearrangement allows for the novel and SOCl2-induced divergent synthesis of 3-methylthioquinolin-2-ones and 3-methylthiospiro[4.5]trienones through intramolecular electrophilic cyclization of N-aryl propyamides. DMSO acts as both solvent and sulfur source, and use of DMSO-h6/d6 enables the incorporation of SCH3 or SCD3 moieties to the 3-position of the heterocyclic framework. Different para-substituents trigger divergent reaction pathways leading to the formation of quinolin-2-ones for mild substituents and spiro[4,5]trienones for both electron-withdrawing and -donating substituents, respectively. On the basis of both computational and experimental results, a new mechanism has been put forward that accounts for the exclusive spirolization/defluorination process and the surprising substituent effects.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Iodocyclization of N-Arylpropynamides Mediated by Hypervalent Iodine Reagent: Divergent Synthesis of Iodinated Quinolin-2-ones and Spiro[4,5]trienones.Org Lett. 2017 Jan 6;19(1):150-153. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.6b03455. Epub 2016 Dec 21. Org Lett. 2017. PMID: 28001422
-
Intramolecular ipso-halocyclization of 4-(p-unsubstituted-aryl)-1-alkynes leading to spiro[4,5]trienones: scope, application, and mechanistic investigations.J Org Chem. 2012 Mar 16;77(6):2837-49. doi: 10.1021/jo300037n. Epub 2012 Mar 7. J Org Chem. 2012. PMID: 22360308
-
Synthesis of Spiro[5.5]trienones- and Spiro[4.5]trienones-Fused Selenocyanates via Electrophilic Selenocyanogen Cyclization and Dearomative Spirocyclization.J Org Chem. 2022 Oct 7;87(19):13089-13101. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.2c01594. Epub 2022 Sep 28. J Org Chem. 2022. PMID: 36170059
-
Synthesis of Seleno-Dibenzocycloheptenones/Spiro[5.5]Trienones by Radical Cyclization of Biaryl Ynones.J Org Chem. 2022 Mar 18;87(6):4273-4283. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.1c03112. Epub 2022 Mar 4. J Org Chem. 2022. PMID: 35245049
-
Recent Advances in DMSO-Based Direct Synthesis of Heterocycles.Molecules. 2022 Dec 2;27(23):8480. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238480. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500564 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in the Use of Dimethyl Sulfoxide as a Synthon in Organic Chemistry.Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2022 Oct 28;380(6):55. doi: 10.1007/s41061-022-00411-8. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2022. PMID: 36306032 Review.
References
-
- Khan S. R.; Mhaka A.; Pili R.; Isaacs J. T. Modified synthesis and antiangiogenic activity of linomide. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2001, 11, 451–452. 10.1016/S0960-894X(00)00699-5. - DOI - PubMed
- Jonsson S.; Andersson G.; Fex T.; Fristedt T.; Hedlund G.; Jansson K.; Abramo L.; Fritzson I.; Pekarski O.; Runstrom A.; Sandin H.; Thuvesson I.; Bjork A. Synthesis and biological evaluation of new 1,2-dihydro-4-hydroxy-2-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxamides for treatment of autoimmune disorders: structure-activity relationship. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 2075–2088. 10.1021/jm031044w. - DOI - PubMed
- Natsugari H.; Ikeura Y.; Kiyota Y.; Ishichi Y.; Ishimaru T.; Saga O.; Shirafuji H.; Tanaka T.; Kamo I.; Doi T.; Otsuka M. Novel, potent, and orally-active substance-P antagonists-synthesis and antagonist activity of N-benzylcarboxamide derivatives of pyrido [3,4-b] pyridine. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 3106–3120. 10.1021/jm00016a014. - DOI - PubMed
- Řehulka J.; Vychodilová K.; Krejčí P.; Gurská S.; Hradil P.; Hajdúch M.; Džubák P.; Hlaváč J. Fluorinated derivatives of 2-phenyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-quinolinone as tubulin polymerization inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 192, 112176.10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112176. - DOI - PubMed
-
- DeVita R. J.; Hollings D. D.; Goulet M. T.; Wyvratt M. J.; Fisher M. H.; Lo J. L.; Yang Y. T.; Cheng K.; Smith R. G. Identification and initial structure-activity relationships of a novel non-peptide quinolone GnRH receptor antagonist. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1999, 9, 2615–2620. 10.1016/S0960-894X(99)00446-1. - DOI - PubMed
- Aleksic M.; Bertosa B.; Nhili R.; Uzelac L.; Jarak I.; Depauw S.; David-Cordonnier M. H.; Kralj M.; Tomic S.; Karminski-Zamola G. Novel substituted benzothiophene and thienothiophene carboxanilides and quinolones: synthesis, photochemical synthesis, DNA-binding properties, antitumor evaluation and 3D-derived QSAR analysis. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 5044–5060. 10.1021/jm300505h. - DOI - PubMed
- Lee J.-F.; Chang T.-Y.; Liu Z.-F.; Lee N.-Z.; Yeh Y.-H.; Chen Y.-S.; Chen T.-C.; Chou H.-S.; Li T.-K.; Lee S.-B.; Lin M.-H. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of heterotetracyclic quinolinone derivatives as anticancer agents targeting topoisomerases. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 190, 112074.10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112074. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tedesco R.; Shaw A. N.; Bambal R.; Chai D. P.; Concha N. O.; Darcy M. G.; Dhanak D.; Fitch D. M.; Gates A.; Gerhardt W. G.; Halegoua D. L.; Han C.; Hofmann G. A.; Johnston V. K.; Kaura A. C.; Liu N. N.; Keenan R. M.; Lin-Goerke J.; Sarisky R. T.; Wiggall K. J.; Zimmerman M. N.; Duffy K. J. 3-(1,1-Dioxo-2H-(1,2,4)-benzothiadiazin-3-yl)-4-hydroxy-2(1H)-quinolinones, potent inhibitors of hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 971–983. 10.1021/jm050855s. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Crawley G. C.; Briggs M. T.; Dowell R. I.; Edwards P. N.; Hamilton P. M.; Kingston J. F.; Oldham K.; Waterson D.; Whalley D. P. 4-Methoxy-2-methyltetrahydropyrans-chiral leukotriene biosynthesis inhibitors, related to ICI D2138, which display enantioselectivity. J. Med. Chem. 1993, 36, 295–296. 10.1021/jm00054a016. - DOI - PubMed
- Shiro T.; Takahashi H.; Kakiguchi K.; Inoue Y.; Masuda K.; Nagata H.; Tobe M. Synthesis and SAR study of imidazoquinolines as a novel structural class of microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase-1 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 285–288. 10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.11.015. - DOI - PubMed
- Shiro T.; Kakiguchi K.; Takahashi H.; Nagata H.; Tobe M. Synthesis and biological evaluation of substituted imidazoquinoline derivatives as mPGES-1 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 2068–2078. 10.1016/j.bmc.2013.01.018. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ikuma Y.; Hochigai H.; Kimura H.; Nunami N.; Kobayashi T.; Uchiyama K.; Furuta Y.; Sakai M.; Horiguchi M.; Masui Y.; Okazaki K.; Sato Y.; Nakahira H. Discovery of 3H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4(5H)-ones as potent and selective dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-4) inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 5864–5883. 10.1016/j.bmc.2012.07.046. - DOI - PubMed
- Ikuma Y.; Nakahira H. Preparation of 2-aminosubstituted 3H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4(5H)-ones by palladium-assisted internal biaryl coupling reaction. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 9509–9517. 10.1016/j.tet.2011.10.015. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

