Structural and Functional Alterations in Visual Pathway After Optic Neuritis in MOG Antibody Disease: A Comparative Study With AQP4 Seropositive NMOSD
- PMID: 34177778
- PMCID: PMC8220215
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.673472
Structural and Functional Alterations in Visual Pathway After Optic Neuritis in MOG Antibody Disease: A Comparative Study With AQP4 Seropositive NMOSD
Abstract
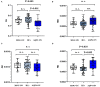
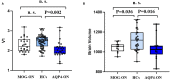
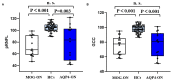
Background: Optic neuritis (ON) is an important clinical manifestation of neuromyelitis optic spectrum disease (NMOSD). Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) antibody-related and aquaporin 4 (AQP4) antibody-related ON show different disease patterns. The aim of this study was to explore the differences in structure and function of the visual pathway in patients with ON associated with MOG and AQP4 antibodies. Methods: In this prospective study, we recruited 52 subjects at Beijing Tiantan Hospital, including 11 with MOG Ig+ ON (MOG-ON), 13 with AQP4 Ig+ ON (AQP4-ON), and 28 healthy controls (HCs). Fractional anisotropy (FA), mean diffusivity (MD), axial diffusivity (AD), and radial diffusivity (RD) of optic radiation (OR), primary visual cortex volume (V1), brain volume, and visual acuity (VA) were compared among groups. A multiple linear regression was used to explore associations between VA and predicted factors. In addition, we used optical coherence tomography (OCT) to examine thickness of the peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer (pRNFL) and retinal ganglion cell complex (GCC) in a separate cohort consisting of 15 patients with ON (8 MOG-ON and 7 AQP4-ON) and 28 HCs. Results: Diffusion tensor imaging showed that the FA of OR was lower than controls in patients with AQP4-ON (p = 0.001) but not those with MOG-ON (p = 0.329) and was significantly different between the latter two groups (p = 0.005), while V1 was similar in patients with MOG-ON and AQP4-ON (p = 0.122), but was lower than controls in AQP4-ON (p = 0.002) but not those with MOG-ON (p = 0.210). The VA outcomes were better in MOG-ON than AQP4-ON, and linear regression analysis revealed that VA in MOG-ON and AQP4-ON was both predicted by the FA of OR (standard β = -0.467 and -0.521, p = 0.036 and 0.034). Both patients of MOG-ON and AQP4-ON showed neuroaxonal damage in the form of pRNFL and GCC thinning but showed no statistically significant difference (p = 0.556, 0.817). Conclusion: The structural integrity of OR in patients with MOG-ON, which is different from the imaging manifestations of AQP4-ON, may be a reason for the better visual outcomes of patients with MOG-ON.
Keywords: AQP4-ON; MOG-ON; diffusion tensor imaging; optic radiation; optical coherence tomography; visual acuity.
Copyright © 2021 Gao, Zhuo, Duan, Yao, Su, Zhang and Song.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MOG-IgG in NMO and related disorders: a multicenter study of 50 patients. Part 4: Afferent visual system damage after optic neuritis in MOG-IgG-seropositive versus AQP4-IgG-seropositive patients.J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Nov 1;13(1):282. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0720-6. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 27802824 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical characteristics and prognosis of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-seropositive paediatric optic neuritis in China.Br J Ophthalmol. 2019 Jun;103(6):831-836. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2018-312399. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Br J Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 30049802
-
AQP4-IgG and MOG-IgG Related Optic Neuritis-Prevalence, Optical Coherence Tomography Findings, and Visual Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Neurol. 2020 Oct 8;11:540156. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.540156. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33132999 Free PMC article.
-
Retina thickness in clinically affected and unaffected eyes in patients with aquaporin-4 immunoglobulin G antibody seropositive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Neurol. 2023 Feb;270(2):759-768. doi: 10.1007/s00415-022-11482-4. Epub 2022 Nov 10. J Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36355186 Review.
-
Epidemiology of Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder and Its Prevalence and Incidence Worldwide.Front Neurol. 2020 Jun 26;11:501. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00501. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32670177 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Features and Imaging Findings of Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein-IgG-Associated Disorder (MOGAD).Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Mar 15;14:850743. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.850743. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35370624 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The influence of MOGAD on diagnosis of multiple sclerosis using MRI.Nat Rev Neurol. 2024 Oct;20(10):620-635. doi: 10.1038/s41582-024-01005-2. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Nat Rev Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39227463 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

