Inflammation, epigenetics, and metabolism converge to cell senescence and ageing: the regulation and intervention
- PMID: 34176928
- PMCID: PMC8236488
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-021-00646-9
Inflammation, epigenetics, and metabolism converge to cell senescence and ageing: the regulation and intervention
Abstract
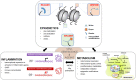
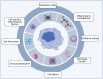
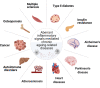
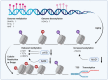
Remarkable progress in ageing research has been achieved over the past decades. General perceptions and experimental evidence pinpoint that the decline of physical function often initiates by cell senescence and organ ageing. Epigenetic dynamics and immunometabolic reprogramming link to the alterations of cellular response to intrinsic and extrinsic stimuli, representing current hotspots as they not only (re-)shape the individual cell identity, but also involve in cell fate decision. This review focuses on the present findings and emerging concepts in epigenetic, inflammatory, and metabolic regulations and the consequences of the ageing process. Potential therapeutic interventions targeting cell senescence and regulatory mechanisms, using state-of-the-art techniques are also discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cellular reprogramming and epigenetic rejuvenation.Clin Epigenetics. 2021 Sep 6;13(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s13148-021-01158-7. Clin Epigenetics. 2021. PMID: 34488874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of epigenetically regulated inflammation in renal diseases.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Feb 15;154(Pt C):295-304. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.10.005. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 36328897 Review.
-
Epigenetic alterations in stem cell ageing-a promising target for age-reversing interventions?Brief Funct Genomics. 2022 Jan 25;21(1):35-42. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elab010. Brief Funct Genomics. 2022. PMID: 33738480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Aspects of Senescence and Organismal Ageing-DNA Damage Response, Telomeres, Inflammation and Chromatin.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 8;22(2):590. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020590. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33435578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic reprogramming as a key to reverse ageing and increase longevity.Ageing Res Rev. 2024 Mar;95:102204. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102204. Epub 2024 Jan 23. Ageing Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 38272265 Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling Histone Loss in Aging and Senescence.Cells. 2024 Feb 9;13(4):320. doi: 10.3390/cells13040320. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38391933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FBLN5 was Regulated by PRDM9, and Promoted Senescence and Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024;19(3):417-425. doi: 10.2174/1574888X18666230822100054. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 37608663 Free PMC article.
-
A new model and precious tool to study molecular mechanisms of macrophage aging.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Oct 3;16(19):12697-12725. doi: 10.18632/aging.206124. Epub 2024 Oct 3. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 39373702 Free PMC article.
-
The connection between aging, cellular senescence and gut microbiome alterations: A comprehensive review.Aging Cell. 2024 Oct;23(10):e14315. doi: 10.1111/acel.14315. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Aging Cell. 2024. PMID: 39148278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond MACE: a multidimensional approach to outcomes in clinical trials for older adults with stable ischemic heart disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Nov 17;10:1276370. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1276370. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 38045910 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

