Dysfunction of the Glymphatic System as a Potential Mechanism of Perioperative Neurocognitive Disorders
- PMID: 34163349
- PMCID: PMC8215113
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.659457
Dysfunction of the Glymphatic System as a Potential Mechanism of Perioperative Neurocognitive Disorders
Abstract
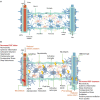
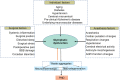
Perioperative neurocognitive disorder (PND) frequently occurs in the elderly as a severe postoperative complication and is characterized by a decline in cognitive function that impairs memory, attention, and other cognitive domains. Currently, the exact pathogenic mechanism of PND is multifaceted and remains unclear. The glymphatic system is a newly discovered glial-dependent perivascular network that subserves a pseudo-lymphatic function in the brain. Recent studies have highlighted the significant role of the glymphatic system in the removal of harmful metabolites in the brain. Dysfunction of the glymphatic system can reduce metabolic waste removal, leading to neuroinflammation and neurological disorders. We speculate that there is a causal relationship between the glymphatic system and symptomatic progression in PND. This paper reviews the current literature on the glymphatic system and some perioperative factors to discuss the role of the glymphatic system in PND.
Keywords: glymphatic system; perioperative neurocognitive disorders; postoperative cognitive dysfunction; postoperative complications; postoperative neuropathy.
Copyright © 2021 Ren, Liu, Lian, Li, Li, Li and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Surgery induces neurocognitive disorder via neuroinflammation and glymphatic dysfunction in middle-aged mice with brain lymphatic drainage impairment.Front Neurosci. 2024 Jun 20;18:1426718. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1426718. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38975244 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term isoflurane anesthesia induces cognitive deficits via AQP4 depolarization mediated blunted glymphatic inflammatory proteins clearance.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024 Aug;44(8):1450-1466. doi: 10.1177/0271678X241237073. Epub 2024 Mar 5. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024. PMID: 38443763 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Perioperative Sleep Disturbance in Postoperative Neurocognitive Disorders.Nat Sci Sleep. 2021 Aug 6;13:1395-1410. doi: 10.2147/NSS.S320745. eCollection 2021. Nat Sci Sleep. 2021. PMID: 34393534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Glymphatic System in Central Nervous System Health and Disease: Past, Present, and Future.Annu Rev Pathol. 2018 Jan 24;13:379-394. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathol-051217-111018. Annu Rev Pathol. 2018. PMID: 29195051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The glymphatic pathway in neurological disorders.Lancet Neurol. 2018 Nov;17(11):1016-1024. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30318-1. Lancet Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30353860 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The nuts and bolts of multimodal anaesthesia in the 21st century: a primer for clinicians.Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2023 Dec 1;36(6):666-675. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0000000000001308. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 37724595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Semi-automated Segmentation and Quantification of Perivascular Spaces at 7 Tesla in COVID-19.Front Neurol. 2022 Apr 1;13:846957. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.846957. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35432151 Free PMC article.
-
Surgery induces neurocognitive disorder via neuroinflammation and glymphatic dysfunction in middle-aged mice with brain lymphatic drainage impairment.Front Neurosci. 2024 Jun 20;18:1426718. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1426718. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38975244 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly rats dependent on NLRP3 activation.Metab Brain Dis. 2024 Nov 13;40(1):1. doi: 10.1007/s11011-024-01425-5. Metab Brain Dis. 2024. PMID: 39535569
-
Influencing factors of glymphatic system during perioperative period.Front Neurosci. 2024 Sep 12;18:1428085. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1428085. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39328423 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amiry-Moghaddam M., Otsuka T., Hurn P. D., Traystman R. J., Haug F. M., Froehner S. C., et al. . (2003). An alpha-syntrophin-dependent pool of AQP4 in astroglial end-feet confers bidirectional water flow between blood and brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 2106–2111. 10.1073/pnas.0437946100 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

