Detection of Serum Cross-Reactive Antibodies and Memory Response to SARS-CoV-2 in Prepandemic and Post-COVID-19 Convalescent Samples
- PMID: 34161567
- PMCID: PMC8557674
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiab333
Detection of Serum Cross-Reactive Antibodies and Memory Response to SARS-CoV-2 in Prepandemic and Post-COVID-19 Convalescent Samples
Abstract
Background: A notable feature of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is that children are less susceptible to severe disease. Children are known to experience more infections with endemic human coronaviruses (HCoVs) compared to adults. Little is known whether HCoV infections lead to cross-reactive anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) antibodies.
Methods: We investigated the presence of cross-reactive anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies to spike 1 (S1), S1-receptor-binding domain (S1-RBD), and nucleocapsid protein (NP) by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays, and neutralizing activity by a SARS-CoV-2 pseudotyped virus neutralization assay, in prepandemic sera collected from children (n = 50) and adults (n = 45), and compared with serum samples from convalescent COVID-19 patients (n = 16).
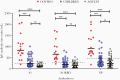
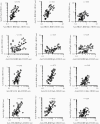
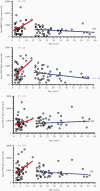
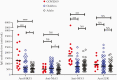
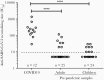
Results: A significant proportion of children (up to 40%) had detectable cross-reactive antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 S1, S1-RBD, and NP antigens, and the anti-S1 and anti-S1-RBD antibody levels correlated with anti-HCoV-HKU1 and anti-HCoV-OC43 S1 antibody titers in prepandemic samples (P < .001). There were marked increases of anti-HCoV-HKU1 and - OC43 S1 (but not anti-NL63 and -229E S1-RBD) antibody titers in serum samples from convalescent COVID-19 patients (P < .001), indicating an activation of cross-reactive immunological memory to β-coronavirus spike.
Conclusions: We demonstrated cross-reactive anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in prepandemic serum samples from children and young adults. Promoting this cross-reactive immunity and memory response derived from common HCoV may be an effective strategy against SARS-COV-2 and future novel coronaviruses.
Keywords: 19; 2; COVID; CoV; HCoV; NL63; SARS; common human coronavirus (HCoV)-HKU1; cross; immunological memory; reactive immunity; serum antibody.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures


Comment in
-
Seasonal Coronavirus Pneumonia After SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Vaccination: New Frenemies?J Infect Dis. 2022 Feb 15;225(4):741-743. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiab421. J Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 34414421 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Cross-reactive antibody against human coronavirus OC43 spike protein correlates with disease severity in COVID-19 patients: a retrospective study.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021 Dec;10(1):664-676. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2021.1905488. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2021. PMID: 33734013 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody Mediated Immunity to SARS-CoV-2 and Human Coronaviruses: Multiplex Beads Assay and Volumetric Absorptive Microsampling to Generate Immune Repertoire Cartography.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 27;12:696370. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.696370. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34386006 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-RBD IgG antibodies from endemic coronaviruses do not protect against the acquisition of SARS-CoV-2 infection among exposed uninfected individuals.Front Immunol. 2024 May 23;15:1396603. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1396603. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38846944 Free PMC article.
-
An overview on the seven pathogenic human coronaviruses.Rev Med Virol. 2022 Mar;32(2):e2282. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2282. Epub 2021 Aug 2. Rev Med Virol. 2022. PMID: 34339073 Review.
-
Evolutionary trajectory of SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variants.Virol J. 2021 Aug 13;18(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s12985-021-01633-w. Virol J. 2021. PMID: 34389034 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Flow Cytometry-Based Measurement of Antibodies Specific for Cell Surface-Expressed Folded SARS-CoV-2 Receptor-Binding Domains.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Apr 1;12(4):377. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12040377. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675759 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-Reactivity of Human, Wild Boar, and Farm Animal Sera from Pre- and Post-Pandemic Periods with Alpha- and Βeta-Coronaviruses (CoV), including SARS-CoV-2.Viruses. 2023 Dec 23;16(1):34. doi: 10.3390/v16010034. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38257734 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an instrument-free and low-cost ELISA dot-blot test to detect antibodies against SARS-CoV-2.Open Life Sci. 2023 Aug 9;18(1):20220577. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0577. eCollection 2023. Open Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37589006 Free PMC article.
-
Differences among epitopes recognized by neutralizing antibodies induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection or COVID-19 vaccination.iScience. 2023 Jun 25;26(7):107208. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107208. eCollection 2023 Jul 21. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37448563 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses in Pediatric Patients: A Bibliometric Analysis.Biomedicines. 2023 May 16;11(5):1455. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11051455. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37239126 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Paules CI, Marston HD, Fauci AS. Coronavirus infections—more than just the common cold. JAMA 2020; 323:707–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

