SUVA: splicing site usage variation analysis from RNA-seq data reveals highly conserved complex splicing biomarkers in liver cancer
- PMID: 34152934
- PMCID: PMC8682974
- DOI: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1940037
SUVA: splicing site usage variation analysis from RNA-seq data reveals highly conserved complex splicing biomarkers in liver cancer
Abstract
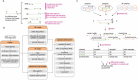
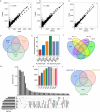
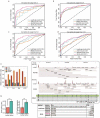
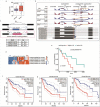
Most of the current alternative splicing (AS) analysis tools are powerless to analyse complex splicing. To address this, we developed SUVA (Splice sites Usage Variation Analysis) that decomposes complex splicing events into five types of splice junction pairs. By analysing real and simulated data, SUVA showed higher sensitivity and accuracy in detecting AS events than the compared methods. Notably, SUVA detected extensive complex AS events and screened out 69 highly conserved and dominant AS events associated with cancer. The cancer-associated complex AS events in FN1 and the co-regulated RNA-binding proteins were significantly correlated with patient survival.
Keywords: Alternative splicing; as; complex splicing; fn1; liver cancer; splicing biomarker; splicing site usage.
Figures


Similar articles
-
PCBP1 regulates the transcription and alternative splicing of metastasis‑related genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2021 Dec 2;11(1):23356. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02642-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34857818 Free PMC article.
-
Study of prognostic splicing factors in cancer using machine learning approaches.Hum Mol Genet. 2024 Jun 21;33(13):1131-1141. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddae047. Hum Mol Genet. 2024. PMID: 38538560
-
TF-RBP-AS Triplet Analysis Reveals the Mechanisms of Aberrant Alternative Splicing Events in Kidney Cancer: Implications for Their Possible Clinical Use as Prognostic and Therapeutic Biomarkers.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 16;22(16):8789. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168789. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445498 Free PMC article.
-
The Detection and Bioinformatic Analysis of Alternative 3' UTR Isoforms as Potential Cancer Biomarkers.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 18;22(10):5322. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105322. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34070203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiplexed primer extension sequencing: A targeted RNA-seq method that enables high-precision quantitation of mRNA splicing isoforms and rare pre-mRNA splicing intermediates.Methods. 2020 Apr 1;176:34-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2019.05.013. Epub 2019 May 21. Methods. 2020. PMID: 31121301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LncRNA TP53TG1 plays an anti-oncogenic role in cervical cancer by synthetically regulating transcriptome profile in HeLa cells.Front Genet. 2022 Oct 4;13:981030. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.981030. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36267418 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-binding proteins potentially regulate the alternative splicing of apoptotic genes during knee osteoarthritis progression.BMC Genomics. 2024 Mar 19;25(1):293. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10181-w. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38504181 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and analysis of epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related RNA-binding proteins and alternative splicing in a human breast cancer cell line.Sci Rep. 2024 May 23;14(1):11753. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62681-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38783078 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-binding proteins potentially regulate alternative splicing of immune/inflammatory-associated genes during the progression of generalized pustular psoriasis.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 Aug 19;316(8):538. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03283-8. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 39158708
-
Genome-wide analysis of dysregulated RNA-binding proteins and alternative splicing genes in keloid.Front Genet. 2023 Jan 26;14:1118999. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1118999. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36777722 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Black DL. Protein diversity from alternative splicing: a challenge for bioinformatics and post-genome biology. Cell. 2000;103(3):367–370. - PubMed
-
- Blencowe BJ. Alternative splicing: new insights from global analyses. Cell. 2006;126(1):37–47. - PubMed
-
- Pan Q, Shai O, Lee LJ, et al. Deep surveying of alternative splicing complexity in the human transcriptome by high-throughput sequencing. Nat Genet. 2008;40(12):1413–1415. - PubMed
-
- Sultan M, Schulz MH, Richard H, et al. A global view of gene activity and alternative splicing by deep sequencing of the human transcriptome. Science (New York, NY). 2008;321(5891):956–960. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
