RSF1 in cancer: interactions and functions
- PMID: 34147108
- PMCID: PMC8214769
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-021-02012-9
RSF1 in cancer: interactions and functions
Abstract
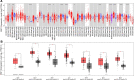
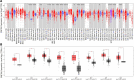
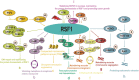
RSF1, remodelling and spacing factor 1, is an important interphase centromere protein and is overexpressed in many types of cancers and correlated with poor overall survival. RSF1 has functions mainly in maintaining chromosome stability, facilitating DNA repair, maintaining the protein homeostasis of RSF1 and suppressing the transcription of some oncogenes when RSF1 protein is expressed at an optimal level; however, RSF1 overexpression facilitates drug resistance and cell cycle checkpoint inhibition to prompt cancer proliferation and survival. The RSF1 expression level and gene background are crucial for RSF1 functions, which may explain why RSF1 has different functions in different cancer types. This review summarizes the functional domains of RSF1, the overexpression status of RSF1 and SNF2H in cancer based on the TCGA and GTEX databases, the cancer-related functions of RSF1 in interacting with H2Aub, HDAC1, CENP-A, PLK1, ATM, CENP-S, SNF2H, HBX, BubR1, cyclin E1, CBP and NF-κB and the potential clinical value of RSF1, which will lay a theoretical foundation for the structural biology study of RSF1 and application of RSF1 inhibitors, truncated RSF1 proteins and SNF2H inhibitors in the treatment of RSF1-overexpressing tumours.
Keywords: CENP-A; H2Aub; NF-κB; PLK1; RSF1; SNF2H.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
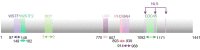
Similar articles
-
RSF1 regulates the proliferation and paclitaxel resistance via modulating NF-κB signaling pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.J Cancer. 2017 Feb 9;8(3):354-362. doi: 10.7150/jca.16720. eCollection 2017. J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28261335 Free PMC article.
-
The chromatin remodeller RSF1 is essential for PLK1 deposition and function at mitotic kinetochores.Nat Commun. 2015 Aug 10;6:7904. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8904. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26259146 Free PMC article.
-
Rsf‑1 regulates malignant melanoma cell viability and chemoresistance via NF‑κB/Bcl‑2 signaling.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Oct;20(4):3487-3498. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10610. Epub 2019 Aug 23. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31485613 Free PMC article.
-
Non-mitotic functions of polo-like kinases in cancer cells.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021 Jan;1875(1):188467. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188467. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33171265 Review.
-
Guarding the Genome: CENP-A-Chromatin in Health and Cancer.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jul 16;11(7):810. doi: 10.3390/genes11070810. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32708729 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pan-cancer analysis of post-translational modifications reveals shared patterns of protein regulation.Cell. 2023 Aug 31;186(18):3945-3967.e26. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.07.013. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Cell. 2023. PMID: 37582358 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing: a new approach for overcoming drug resistance in cancer.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022 Jun 17;27(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00348-2. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35715750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potentials and future perspectives of multi-target drugs in cancer treatment: the next generation anti-cancer agents.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Apr 15;22(1):228. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01607-9. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38622735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High expression of RNF169 is associated with poor prognosis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma by regulating tumour immune infiltration.Front Genet. 2023 Jan 5;13:1022626. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1022626. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36685833 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of Chromatin Remodeling Complexes in Ovarian Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 8;23(22):13670. doi: 10.3390/ijms232213670. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430148 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Simpson B, Basit H, Al Aboud NM. Genetics, DNA Packaging. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2021. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

