Role of DAMPs in respiratory virus-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome-with a preliminary reference to SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia
- PMID: 34140652
- PMCID: PMC8210526
- DOI: 10.1038/s41435-021-00140-w
Role of DAMPs in respiratory virus-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome-with a preliminary reference to SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Role of DAMPs in respiratory virus-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome - with a preliminary reference to SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia.Genes Immun. 2022 Dec;23(8):245. doi: 10.1038/s41435-022-00190-8. Genes Immun. 2022. PMID: 36456661 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
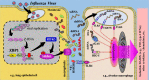
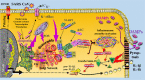
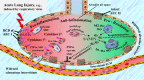
When surveying the current literature on COVID-19, the "cytokine storm" is considered to be pathogenetically involved in its severe outcomes such as acute respiratory distress syndrome, systemic inflammatory response syndrome, and eventually multiple organ failure. In this review, the similar role of DAMPs is addressed, that is, of those molecules, which operate upstream of the inflammatory pathway by activating those cells, which ultimately release the cytokines. Given the still limited reports on their role in COVID-19, the emerging topic is extended to respiratory viral infections with focus on influenza. At first, a brief introduction is given on the function of various classes of activating DAMPs and counterbalancing suppressing DAMPs (SAMPs) in initiating controlled inflammation-promoting and inflammation-resolving defense responses upon infectious and sterile insults. It is stressed that the excessive emission of DAMPs upon severe injury uncovers their fateful property in triggering dysregulated life-threatening hyperinflammatory responses. Such a scenario may happen when the viral load is too high, for example, in the respiratory tract, "forcing" many virus-infected host cells to decide to commit "suicidal" regulated cell death (e.g., necroptosis, pyroptosis) associated with release of large amounts of DAMPs: an important topic of this review. Ironically, although the aim of this "suicidal" cell death is to save and restore organismal homeostasis, the intrinsic release of excessive amounts of DAMPs leads to those dysregulated hyperinflammatory responses-as typically involved in the pathogenesis of acute respiratory distress syndrome and systemic inflammatory response syndrome in respiratory viral infections. Consequently, as briefly outlined in this review, these molecules can be considered valuable diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers to monitor and evaluate the course of the viral disorder, in particular, to grasp the eventual transition precociously from a controlled defense response as observed in mild/moderate cases to a dysregulated life-threatening hyperinflammatory response as seen, for example, in severe/fatal COVID-19. Moreover, the pathogenetic involvement of these molecules qualifies them as relevant future therapeutic targets to prevent severe/ fatal outcomes. Finally, a theory is presented proposing that the superimposition of coronavirus-induced DAMPs with non-virus-induced DAMPs from other origins such as air pollution or high age may contribute to severe and fatal courses of coronavirus pneumonia.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Innate Receptor Activation Patterns Involving TLR and NLR Synergisms in COVID-19, ALI/ARDS and Sepsis Cytokine Storms: A Review and Model Making Novel Predictions and Therapeutic Suggestions.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 20;22(4):2108. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042108. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33672738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammation resolution: a dual-pronged approach to averting cytokine storms in COVID-19?Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020 Jun;39(2):337-340. doi: 10.1007/s10555-020-09889-4. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020. PMID: 32385712 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment with soluble CD24 attenuates COVID-19-associated systemic immunopathology.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Jan 10;15(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01222-y. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35012610 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Targeting inflammatory cytokine storm to fight against COVID-19 associated severe complications.Life Sci. 2021 Feb 15;267:118923. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118923. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33358906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytokines and Chemokines in SARS-CoV-2 Infections-Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Cytokine Storm.Biomolecules. 2021 Jan 12;11(1):91. doi: 10.3390/biom11010091. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33445810 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Cancer and COVID-19 as Associated with Oxidative Stress.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Jan 19;11(2):218. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11020218. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36851096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma gp96 is a Novel Predictive Biomarker for Severe COVID-19.Microbiol Spectr. 2021 Dec 22;9(3):e0059721. doi: 10.1128/Spectrum.00597-21. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Microbiol Spectr. 2021. PMID: 34817280 Free PMC article.
-
HMGB1: A Potential Target of Nervus Vagus Stimulation in Pediatric SARS-CoV-2-Induced ALI/ARDS.Front Pediatr. 2022 May 11;10:884539. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.884539. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35633962 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19-Induced Myocarditis: Pathophysiological Roles of ACE2 and Toll-like Receptors.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 11;24(6):5374. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065374. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fungal Infections in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients: Inevitabile Malum.J Clin Med. 2022 Apr 4;11(7):2017. doi: 10.3390/jcm11072017. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35407625 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen L, Long X, Xu Q, Tan J, Wang G, Cao Y, et al. Elevated serum levels of S100A8/A9 and HMGB1 at hospital admission are correlated with inferior clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients. Cell Mol Immunol. 2020;17:992–4. Available from: http://www.nature.com/articles/s41423-020-0492-x. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scozzi D, Cano M, Ma L, Zhou D, Zhu JH, O’Halloran JA, et al. Circulating mitochondrial DNA is an early indicator of severe illness and mortality from COVID-19. JCI Insight. 2021. http://insight.jci.org/articles/view/143299. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Matzinger P. Tolerance, Danger, and the Extended Family. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:991–1045. - PubMed
-
- Land W, Schneeberger H, Schleibner S, Illner WD, Abendroth D, Rutili G, et al. The beneficial effect of human recombinant superoxide dismutase on acute and chronic rejection events in recipients of cadaveric renal transplants. Transplant. 1994;57:211–7. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199401001-00010. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

