Norstictic Acid Is a Selective Allosteric Transcriptional Regulator
- PMID: 34137598
- PMCID: PMC8717358
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.1c03258
Norstictic Acid Is a Selective Allosteric Transcriptional Regulator
Abstract
Inhibitors of transcriptional protein-protein interactions (PPIs) have high value both as tools and for therapeutic applications. The PPI network mediated by the transcriptional coactivator Med25, for example, regulates stress-response and motility pathways, and dysregulation of the PPI networks contributes to oncogenesis and metastasis. The canonical transcription factor binding sites within Med25 are large (∼900 Å2) and have little topology, and thus, they do not present an array of attractive small-molecule binding sites for inhibitor discovery. Here we demonstrate that the depsidone natural product norstictic acid functions through an alternative binding site to block Med25-transcriptional activator PPIs in vitro and in cell culture. Norstictic acid targets a binding site comprising a highly dynamic loop flanking one canonical binding surface, and in doing so, it both orthosterically and allosterically alters Med25-driven transcription in a patient-derived model of triple-negative breast cancer. These results highlight the potential of Med25 as a therapeutic target as well as the inhibitor discovery opportunities presented by structurally dynamic loops within otherwise challenging proteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

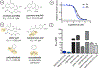
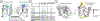
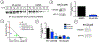
Similar articles
-
A Lipopeptidomimetic of Transcriptional Activation Domains Selectively Disrupts the Coactivator Med25 Protein-Protein Interactions.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2024 May 21;63(21):e202400781. doi: 10.1002/anie.202400781. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2024. PMID: 38527936 Free PMC article.
-
Conservation of coactivator engagement mechanism enables small-molecule allosteric modulators.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Sep 4;115(36):8960-8965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1806202115. Epub 2018 Aug 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30127017 Free PMC article.
-
The Mediator complex subunit MED25 is targeted by the N-terminal transactivation domain of the PEA3 group members.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 May;41(9):4847-59. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt199. Epub 2013 Mar 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23531547 Free PMC article.
-
The plant Mediator complex and its role in jasmonate signaling.J Exp Bot. 2019 Jul 5;70(13):3415-3424. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz233. J Exp Bot. 2019. PMID: 31089685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Unexpected Encounter: Respiratory Syncytial Virus Nonstructural Protein 1 Interacts with Mediator Subunit MED25.J Virol. 2022 Oct 12;96(19):e0129722. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01297-22. Epub 2022 Sep 14. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 36102648 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Mediator complex as a master regulator of transcription by RNA polymerase II.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Nov;23(11):732-749. doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00498-3. Epub 2022 Jun 20. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 35725906 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Derivatives of the Fungal Natural Product Illudalic Acid Inhibit the Activity of Protein Histidine Phosphatase PHPT1.ChemMedChem. 2023 Aug 1;18(15):e202300187. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202300187. Epub 2023 Jun 16. ChemMedChem. 2023. PMID: 37267298 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of CREB Binding and Function with a Dual-Targeting Ligand.Biochemistry. 2024 Jan 2;63(1):1-8. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.3c00469. Epub 2023 Dec 12. Biochemistry. 2024. PMID: 38086054 Free PMC article.
-
An emerging simple and effective approach to increase the productivity of thraustochytrids microbial lipids by regulating glycolysis process and triacylglycerols' decomposition.Biotechnol Biofuels. 2021 Dec 31;14(1):247. doi: 10.1186/s13068-021-02097-4. Biotechnol Biofuels. 2021. PMID: 34972534 Free PMC article.
-
Drugging Fuzzy Complexes in Transcription.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Dec 21;8:795743. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.795743. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34993233 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sabari BR; Dall’Agnese A; Boija A; Klein IA; Coffey EL; Shrinivas K; Abraham BJ; Hannett NM; Zamudio AV; Manteiga JC; Li CH; Guo YE; Day DS; Schuijers J; Vasile E; Malik S; Hnisz D; Lee TI; Cisse II; Roeder RG; Sharp PA; Chakraborty AK; Young RA Coactivator Condensation at Super-Enhancers Links Phase Separation and Gene Control. Science 2018, 361 (6400), eaar3958. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang F; Vought BW; Satterlee JS; Walker AK; Jim Sun Z-Y; Watts JL; DeBeaumont R; Saito RM; Hyberts SG; Yang S; Macol C; Iyer L; Tjian R; van den Heuvel S; Hart AC; Wagner G; Näär AM An ARC/Mediator Subunit Required for SREBP Control of Cholesterol and Lipid Homeostasis. Nature 2006, 442 (7103), 700–704. - PubMed
-
- Larivière L; Seizl M; Cramer P̀. A Structural Perspective on Mediator Function. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2012, 24 (3), 305–313. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

