ErbB4 in Spinal PV Interneurons Regulates Mechanical Allodynia in Neuropathic Pain via Modulation of Glycinergic Inhibitory Tone
- PMID: 34135628
- PMCID: PMC8200169
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S311894
ErbB4 in Spinal PV Interneurons Regulates Mechanical Allodynia in Neuropathic Pain via Modulation of Glycinergic Inhibitory Tone
Abstract
Background: Mechanical allodynia is the most common and challenging symptom associated with neuropathic pain; however, the underlying mechanisms are still unclear. The aim of this study was to investigate whether ErbB4, a receptor for neuregulin-1 (NRG1), participates in the modulation of mechanical allodynia.
Methods: Radiant heat and von Frey filaments were applied to assess nociceptive behaviors. Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction, Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and small interfering RNA were used to identify the likely mechanisms.
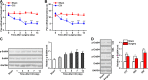
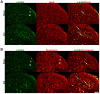
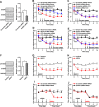
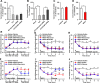
Results: ErbB4 was rapidly and persistently activated in spinal parvalbumin (PV) interneurons after chronic constriction injury (CCI) in mice. Knockdown of ErbB4 in the spinal cord prevented and reversed CCI-induced mechanical allodynia, and activation of ErbB4 by spinal application of NRG1 induced mechanical allodynia in naïve mice. Furthermore, we found that activation of ErbB4 decreased the glycine concentration in the spinal cord, contributing to modulation of mechanical allodynia.
Conclusion: ErbB4 in spinal PV interneurons gates mechanical allodynia in neuropathic pain via regulation of glycinergic inhibitory tone, suggesting that a possible ErbB4-mediated process participates in the development of neuropathic pain.
Keywords: Erb4; glycine; mechanical allodynia; parvalbumin interneuron.
© 2021 Yu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ROR2 modulates neuropathic pain via phosphorylation of NMDA receptor subunit GluN2B in rats.Br J Anaesth. 2019 Aug;123(2):e239-e248. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2018.08.025. Epub 2018 Oct 29. Br J Anaesth. 2019. PMID: 30916039 Free PMC article.
-
NRG1-ErbB signalling promotes microglia activation contributing to incision-induced mechanical allodynia.Eur J Pain. 2015 May;19(5):686-94. doi: 10.1002/ejp.590. Epub 2014 Aug 27. Eur J Pain. 2015. PMID: 25159022
-
Neuregulin-1-ErbB signaling promotes microglia activation contributing to mechanical allodynia of cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis.Neurourol Urodyn. 2019 Jun;38(5):1250-1260. doi: 10.1002/nau.24005. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Neurourol Urodyn. 2019. PMID: 30989724
-
Neuregulin1-ErbB4 Signaling in Spinal Cord Participates in Electroacupuncture Analgesia in Inflammatory Pain.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jan 28;15:636348. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.636348. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33584196 Free PMC article.
-
A feed-forward spinal cord glycinergic neural circuit gates mechanical allodynia.J Clin Invest. 2013 Sep;123(9):4050-62. doi: 10.1172/JCI70026. Epub 2013 Aug 27. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23979158 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Increased Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Levels in Cerebrospinal Fluid During the Acute Phase in TBI-Induced Mechanical Allodynia in the Rat Model.J Pain Res. 2022 Jan 29;15:229-239. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S344110. eCollection 2022. J Pain Res. 2022. PMID: 35125890 Free PMC article.
-
The therapeutic effects of transferring remote ischemic preconditioning serum in rats with neuropathic pain symptoms.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 13;9(10):e20954. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20954. eCollection 2023 Oct. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37867836 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

