A Study of the Identification, Fragmentation Mode and Metabolic Pathways of Imatinib in Rats Using UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS
- PMID: 34123459
- PMCID: PMC8166468
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/8434204
A Study of the Identification, Fragmentation Mode and Metabolic Pathways of Imatinib in Rats Using UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS
Abstract
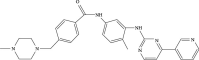
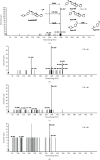
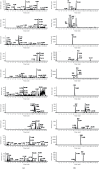
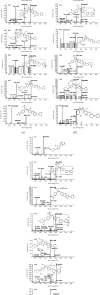
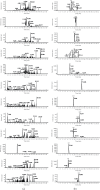
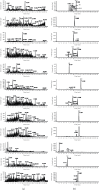
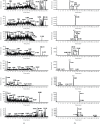
In this study, The metabolites, metabolic pathways, and metabolic fragmentation mode of a tyrosine kinase inhibitor- (TKI-) imatinib in rats were investigated. The samples for analysis were pretreated via solid-phase extraction, and the metabolism of imatinib in rats was studied using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS). Eighteen imatinib metabolites were identified in rat plasma, 21 in bile, 18 in urine, and 12 in feces. Twenty-seven of the above compounds were confirmed as metabolites of imatinib and 9 of them were newly discovered for the first time. Oxidation, hydroxylation, dealkylation, and catalytic dehydrogenation are the main metabolic pathways in phase I. For phase II, the main metabolic pathways were N-acetylation, methylation, cysteine, and glucuronidation binding. The fragment ions of imatinib and its metabolites were confirmed to be produced by the cleavage of the C-N bond at the amide bond. The newly discovered metabolite of imatinib was identified by UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS. The metabolic pathway of imatinib and its fragmentation pattern were summarized. These results could be helpful to study the safety of imatinib for clinical use.
Copyright © 2021 Sijiang Liu and Zhaojin Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comprehensive identification, fragmentation pattern, and metabolic pathways of gefitinib metabolites via UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS: in vivo study of rat plasma, urine, bile, and faeces.Xenobiotica. 2021 Mar;51(3):355-365. doi: 10.1080/00498254.2020.1859642. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Xenobiotica. 2021. PMID: 33269993
-
Rapid screening and identification of metabolites of murpanicin in rats by UHPLC/Q-TOF-MS/MS combined with diagnostic fragment ions (DFIs) and multiple mass defect filter.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2022 May 10;213:114679. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2022.114679. Epub 2022 Feb 21. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2022. PMID: 35228054
-
In vitro and in vivo metabolic investigation of the Palbociclib by UHPLC-Q-TOF/MS/MS and in silico toxicity studies of its metabolites.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Aug 5;157:59-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.05.008. Epub 2018 May 16. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 29772457
-
Metabolites characterization of a novel DPP-4 inhibitor, imigliptin in humans and rats using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with synapt high-resolution mass spectrometry.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Aug 5;157:189-200. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2018.05.029. Epub 2018 May 23. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 29803910 Clinical Trial.
-
Metabolic profile of irisolidone in rats obtained by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013 Dec 15;941:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.09.033. Epub 2013 Oct 7. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 24184829
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
