Hypoxia and Inflammation: Insights From High-Altitude Physiology
- PMID: 34122145
- PMCID: PMC8188852
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.676782
Hypoxia and Inflammation: Insights From High-Altitude Physiology
Abstract
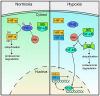
The key regulators of the transcriptional response to hypoxia and inflammation (hypoxia inducible factor, HIF, and nuclear factor-kappa B, NF-κB, respectively) are evolutionarily conserved and share significant crosstalk. Tissues often experience hypoxia and inflammation concurrently at the site of infection or injury due to fluid retention and immune cell recruitment that ultimately reduces the rate of oxygen delivery to tissues. Inflammation can induce activity of HIF-pathway genes, and hypoxia may modulate inflammatory signaling. While it is clear that these molecular pathways function in concert, the physiological consequences of hypoxia-induced inflammation and how hypoxia modulates inflammatory signaling and immune function are not well established. In this review, we summarize known mechanisms of HIF and NF-κB crosstalk and highlight the physiological consequences that can arise from maladaptive hypoxia-induced inflammation. Finally, we discuss what can be learned about adaptive regulation of inflammation under chronic hypoxia by examining adaptive and maladaptive inflammatory phenotypes observed in human populations at high altitude. We aim to provide insight into the time domains of hypoxia-induced inflammation and highlight the importance of hypoxia-induced inflammatory sensitization in immune function, pathologies, and environmental adaptation.
Keywords: high altitude; hypoxia; hypoxia inducible factor; inflammation; nuclear factor-κB.
Copyright © 2021 Pham, Parikh and Heinrich.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inflammatory gene expression during acute high-altitude exposure.J Physiol. 2022 Sep;600(18):4169-4186. doi: 10.1113/JP282772. Epub 2022 Aug 17. J Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35875936 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB alpha derepresses hypoxia-inducible factor-1 during moderate hypoxia by sequestering factor inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor from hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha.FEBS J. 2009 Jul;276(13):3470-80. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07069.x. Epub 2009 May 18. FEBS J. 2009. PMID: 19456861
-
NF-κB and HIF crosstalk in immune responses.FEBS J. 2016 Feb;283(3):413-24. doi: 10.1111/febs.13578. Epub 2015 Nov 24. FEBS J. 2016. PMID: 26513405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Hypoxia/reoxygenation and lipopolysaccharide induced nuclear factor-ΚB and hypoxia-inducible factor-1α signaling pathways in intestinal epithelial cell injury and the interventional effect of emodin].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014 Jun;26(6):409-14. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2014.06.009. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014. PMID: 24912640 Chinese.
-
Chronic and Cycling Hypoxia: Drivers of Cancer Chronic Inflammation through HIF-1 and NF-κB Activation: A Review of the Molecular Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 2;22(19):10701. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910701. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639040 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Live Microscopy of Multicellular Spheroids with the Multimodal Near-Infrared Nanoparticles Reveals Differences in Oxygenation Gradients.ACS Nano. 2024 May 14;18(19):12168-12186. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c12539. Epub 2024 Apr 30. ACS Nano. 2024. PMID: 38687976 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Blood Biomarkers and Potential Therapeutic Agents for Human Acute Mountain Sickness Based on Transcriptomic Analysis, Inflammatory Infiltrates and Molecular Docking.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 21;25(20):11311. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011311. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39457093 Free PMC article.
-
Time Domains of Hypoxia Responses and -Omics Insights.Front Physiol. 2022 Aug 8;13:885295. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.885295. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36035495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia-Induced Inflammation in In Vitro Model of Human Blood-Brain Barrier: Modulatory Effects of the Olfactory Ensheathing Cell-Conditioned Medium.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Oct 7. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04517-6. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39370481
-
Hypoxia adaptation mechanism in rats' peripheral auditory system in high altitude migration: a time series transcriptome analysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 6;14(1):26909. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78169-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39505982 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bärtsch P. (1999). High altitude pulmonary edema. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 31, 23–27. - PubMed

