Nanoparticles: A Hope for the Treatment of Inflammation in CNS
- PMID: 34122112
- PMCID: PMC8187807
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.683935
Nanoparticles: A Hope for the Treatment of Inflammation in CNS
Abstract
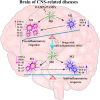
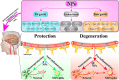
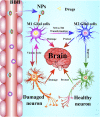
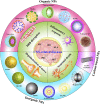
Neuroinflammation, an inflammatory response within the central nervous system (CNS), is a main hallmark of common neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), among others. The over-activated microglia release pro-inflammatory cytokines, which induces neuronal death and accelerates neurodegeneration. Therefore, inhibition of microglia over-activation and microglia-mediated neuroinflammation has been a promising strategy for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Many drugs have shown promising therapeutic effects on microglia and inflammation. However, the blood-brain barrier (BBB)-a natural barrier preventing brain tissue from contact with harmful plasma components-seriously hinders drug delivery to the microglial cells in CNS. As an emerging useful therapeutic tool in CNS-related diseases, nanoparticles (NPs) have been widely applied in biomedical fields for use in diagnosis, biosensing and drug delivery. Recently, many NPs have been reported to be useful vehicles for anti-inflammatory drugs across the BBB to inhibit the over-activation of microglia and neuroinflammation. Therefore, NPs with good biodegradability and biocompatibility have the potential to be developed as an effective and minimally invasive carrier to help other drugs cross the BBB or as a therapeutic agent for the treatment of neuroinflammation-mediated neurodegenerative diseases. In this review, we summarized various nanoparticles applied in CNS, and their mechanisms and effects in the modulation of inflammation responses in neurodegenerative diseases, providing insights and suggestions for the use of NPs in the treatment of neuroinflammation-related neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier; central neural system; nanoparticles; neurodegenerative diseases; neuroinflammation.
Copyright © 2021 Zhu, Hu, Yu, Zhou, Wu, Tang, Qin, Fan and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nanomedicine and its application in treatment of microglia-mediated neuroinflammation.Curr Med Chem. 2014;21(37):4215-26. doi: 10.2174/0929867321666140716101258. Curr Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25039775 Review.
-
Natural products as a potential modulator of microglial polarization in neurodegenerative diseases.Pharmacol Res. 2019 Jul;145:104253. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104253. Epub 2019 May 4. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 31059788 Review.
-
Modulation of Microglial Activity by Rho-Kinase (ROCK) Inhibition as Therapeutic Strategy in Parkinson's Disease and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Front Aging Neurosci. 2017 Apr 4;9:94. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2017.00094. eCollection 2017. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28420986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain and Peripheral Atypical Inflammatory Mediators Potentiate Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration.Front Cell Neurosci. 2017 Jul 24;11:216. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2017.00216. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28790893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifaceted Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Pathophysiological and Therapeutic Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 30;22(3):1413. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031413. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33573368 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Review of the Common Neurodegenerative Disorders: Current Therapeutic Approaches and the Potential Role of Nanotherapeutics.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 6;23(3):1851. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031851. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of a Nanoparticle-Based Approach for the Blood-Brain Barrier Passage in a Murine Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Cells. 2022 Dec 10;11(24):4003. doi: 10.3390/cells11244003. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36552768 Free PMC article.
-
Inorganic Nanomaterials versus Polymer-Based Nanoparticles for Overcoming Neurodegeneration.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Jul 7;12(14):2337. doi: 10.3390/nano12142337. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35889562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opportunities Offered by Graphene Nanoparticles for MicroRNAs Delivery for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Treatment.Materials (Basel). 2021 Dec 24;15(1):126. doi: 10.3390/ma15010126. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35009270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Major Hypotheses of Alzheimer's Disease: Related Nanotechnology-Based Approaches for Its Diagnosis and Treatment.Cells. 2023 Nov 21;12(23):2669. doi: 10.3390/cells12232669. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38067098 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agrawal M., Tripathi D. K., Mourtas S., Saraf S., Antimisiaris S. G., Hammarlund-Udenaes M., et al. (2017). Recent Advancements in Liposomes Targeting Strategies to Cross Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) for the Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease. J. Control. Release 260, 61–77. 10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.05.019 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

