Circular RNA CircHIPK3 Promotes Homeostasis of the Intestinal Epithelium by Reducing MicroRNA 29b Function
- PMID: 34116030
- PMCID: PMC8463477
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.05.060
Circular RNA CircHIPK3 Promotes Homeostasis of the Intestinal Epithelium by Reducing MicroRNA 29b Function
Abstract
Background & aims: Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a class of endogenous noncoding RNAs that form covalently closed circles. Although circRNAs influence many biological processes, little is known about their role in intestinal epithelium homeostasis. We surveyed circRNAs required to maintain intestinal epithelial integrity and identified circular homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 3 (circHIPK3) as a major regulator of intestinal epithelial repair after acute injury.
Methods: Intestinal mucosal tissues were collected from mice exposed to cecal ligation and puncture for 48 hours and patients with inflammatory bowel diseases and sepsis. We isolated primary enterocytes from the small intestine of mice and derived intestinal organoids. The levels of circHIPK3 were silenced in intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) by transfection with small interfering RNAs targeting the circularization junction of circHIPK3 or elevated using a plasmid vector that overexpressed circHIPK3. Intestinal epithelial repair was examined in an in vitro injury model by removing part of the monolayer. The association of circHIPK3 with microRNA 29b (miR-29b) was determined by biotinylated RNA pull-down assays.
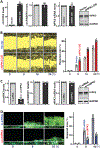
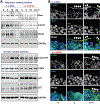
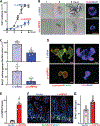
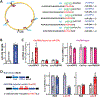
Results: Genome-wide profile analyses identified ∼300 circRNAs, including circHIPK3, differentially expressed in the intestinal mucosa of mice after cecal ligation and puncture relative to sham mice. Intestinal mucosa from patients with inflammatory bowel diseases and sepsis had reduced levels of circHIPK3. Increasing the levels of circHIPK3 enhanced intestinal epithelium repair after wounding, whereas circHIPK3 silencing repressed epithelial recovery. CircHIPK3 silencing also inhibited growth of IECs and intestinal organoids, and circHIPK3 overexpression promoted intestinal epithelium renewal in mice. Mechanistic studies revealed that circHIPK3 directly bound to miR-29b and inhibited miR-29 activity, thus increasing expression of Rac1, Cdc42, and cyclin B1 in IECs after wounding.
Conclusions: In studies of mice, IECs, and human tissues, our results indicate that circHIPK3 improves repair of the intestinal epithelium at least in part by reducing miR-29b availability.
Keywords: CircRNAs; IBD; IEC; MicroRNAs; Mucosal Injury.
Copyright © 2021 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors disclose no conflicts.
Figures

Comment in
-
A Novel Role of Circular RNA in Intestinal Epithelial Repair.Gastroenterology. 2021 Oct;161(4):1108-1110. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.07.031. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Gastroenterology. 2021. PMID: 34303659 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Long Noncoding RNA uc.173 Promotes Renewal of the Intestinal Mucosa by Inducing Degradation of MicroRNA 195.Gastroenterology. 2018 Feb;154(3):599-611. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.10.009. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Gastroenterology. 2018. PMID: 29042220 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of circHIPK3 prevents angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis by sponging miR-29b-3p.Int J Cardiol. 2019 Oct 1;292:188-196. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.04.006. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Int J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30967276
-
CircHIPK3 promotes colorectal cancer growth and metastasis by sponging miR-7.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Apr 1;9(4):417. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0454-8. Cell Death Dis. 2018. Retraction in: Cell Death Dis. 2024 May 29;15(5):372. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06761-z PMID: 29549306 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Development, validation and implementation of an in vitro model for the study of metabolic and immune function in normal and inflamed human colonic epithelium.Dan Med J. 2015 Jan;62(1):B4973. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 25557335 Review.
-
Posttranscriptional Regulation of Intestinal Mucosal Growth and Adaptation by Noncoding RNAs in Critical Surgical Disorders.J Invest Surg. 2024 Dec;37(1):2308809. doi: 10.1080/08941939.2024.2308809. Epub 2024 Feb 7. J Invest Surg. 2024. PMID: 38323630 Review.
Cited by
-
PLGA-microspheres-carried circGMCL1 protects against Crohn's colitis through alleviating NLRP3 inflammasome-induced pyroptosis by promoting autophagy.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Sep 10;13(9):782. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05226-5. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36088391 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging and quantification of human and viral circular RNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Aug 27;52(15):e70. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae583. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39051561 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNAs in organ injury: recent development.J Transl Med. 2022 Nov 18;20(1):533. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03725-9. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36401311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNA ATP2C1 (has_circ_0005797) sponges miR-432/miR-335 to promote breast cancer progression through regulating CCND1 expression.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Aug 15;13(8):3433-3448. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37693160 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Flexibility of Exosomes and MicroRNAs of Intestinal Epithelial Cells in Affecting Inflammation.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 May 11;9:854487. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.854487. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35647030 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Assimakopoulos SF, Triantos C, Thomopoulos K, et al.Gut-origin sepsis in the critically ill patient: pathophysiology and treatment. Infection 2018; 46:751–760. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

