Overexpressed Na V 1.7 Channels Confer Hyperexcitability to in vitro Trigeminal Sensory Neurons of Ca V 2.1 Mutant Hemiplegic Migraine Mice
- PMID: 34113237
- PMCID: PMC8185157
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2021.640709
Overexpressed Na V 1.7 Channels Confer Hyperexcitability to in vitro Trigeminal Sensory Neurons of Ca V 2.1 Mutant Hemiplegic Migraine Mice
Abstract
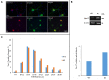
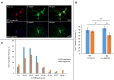
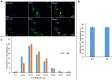
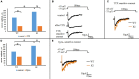
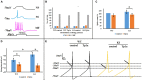
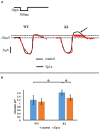
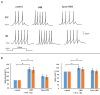
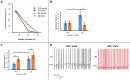
Trigeminal sensory neurons of transgenic knock-in (KI) mice expressing the R192Q missense mutation in the α1A subunit of neuronal voltage-gated Ca V 2.1 Ca2+ channels, which leads to familial hemiplegic migraine type 1 (FHM1) in patients, exhibit a hyperexcitability phenotype. Here, we show that the expression of Na V 1.7 channels, linked to pain states, is upregulated in KI primary cultures of trigeminal ganglia (TG), as shown by increased expression of its α1 subunit. In the majority of TG neurons, Na V 1.7 channels are co-expressed with ATP-gated P2X3 receptors (P2X3R), which are important nociceptive sensors. Reversing the trigeminal phenotype with selective Ca V 2.1 channel inhibitor ω-agatoxin IVA inhibited Na V 1.7 overexpression. Functionally, KI neurons revealed a TTX-sensitive inward current of larger amplitude that was partially inhibited by selective Na V 1.7 blocker Tp1a. Under current-clamp condition, Tp1a raised the spike threshold of both wild-type (WT) and KI neurons with decreased firing rate in KI cells. Na V 1.7 activator OD1 accelerated firing in WT and KI neurons, a phenomenon blocked by Tp1a. Enhanced expression and function of Na V 1.7 channels in KI TG neurons resulted in higher excitability and facilitated nociceptive signaling. Co-expression of Na V 1.7 channels and P2X3Rs in TGs may explain how hypersensitivity to local stimuli can be relevant to migraine.
Keywords: calcium channel; migraine; nociception; purinergic receptors; sodium channel; transgenic mice.
Copyright © 2021 Mehboob, Marchenkova, van den Maagdenberg and Nistri.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Loss of inhibition by brain natriuretic peptide over P2X3 receptors contributes to enhanced spike firing of trigeminal ganglion neurons in a mouse model of familial hemiplegic migraine type-1.Neuroscience. 2016 Sep 7;331:197-205. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.06.034. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Neuroscience. 2016. PMID: 27346147
-
A hyperexcitability phenotype in mouse trigeminal sensory neurons expressing the R192Q Cacna1a missense mutation of familial hemiplegic migraine type-1.Neuroscience. 2014 Apr 25;266:244-54. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.02.020. Epub 2014 Feb 27. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24583041
-
Familial hemiplegic migraine Ca(v)2.1 channel mutation R192Q enhances ATP-gated P2X3 receptor activity of mouse sensory ganglion neurons mediating trigeminal pain.Mol Pain. 2010 Aug 24;6:48. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-6-48. Mol Pain. 2010. PMID: 20735819 Free PMC article.
-
Differential distribution of voltage-gated channels in myelinated and unmyelinated baroreceptor afferents.Auton Neurosci. 2012 Dec 24;172(1-2):4-12. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2012.10.014. Epub 2012 Nov 10. Auton Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 23146622 Review.
-
Calcium channels and synaptic transmission in familial hemiplegic migraine type 1 animal models.Biophys Rev. 2014 Mar;6(1):15-26. doi: 10.1007/s12551-013-0126-y. Epub 2013 Dec 3. Biophys Rev. 2014. PMID: 28509957 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of ATP in migraine mechanisms: focus on P2X3 receptors.J Headache Pain. 2023 Jan 3;24(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s10194-022-01535-4. J Headache Pain. 2023. PMID: 36597043 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

