Prognostic Role of High Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein in Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 34109224
- PMCID: PMC8181755
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.659446
Prognostic Role of High Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein in Patients With Acute Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
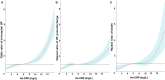
Background: High sensitivity CRP (hs-CRP) has attracted intense interest in risk assessment. We aimed to explore its prognostic value in patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI). Methods and Results: We enrolled 4,504 consecutive AMI patients in this prospective cohort study. The associations between hs-CRP levels with the incidence of in-hospital HF was evaluated by logistic regression analysis. The association between hs-CRP levels and the cumulative incidence of HF after hospitalization were evaluated by Fine-Gray proportional sub-distribution hazards models, accounting for death without HF as competing risk. Cox proportional hazards regression models were constructed to estimate the association between hs-CRP levels and the risk of all-cause mortality. Over a median follow-up of 1 year, 1,112 (24.7%) patients developed in-hospital HF, 571 (18.9%) patients developed HF post-discharge and 262 (8.2%) patients died. In the fully adjusted model, the risk of in-hospital heart failure (HF) [95% confidence intervals (CI)] among those patients with hs-CRP values in quartile 3 (Q3) and Q4 were 1.36 (1.05-1.77) and 1.41 (1.07-1.85) times as high as the risk among patients in Q1 (p trend < 0.001). Patients with hs-CRP values in Q3 and Q4 had 1.33 (1.00-1.76) and 1.80 times (1.37-2.36) as high as the risk of HF post-discharge compared with patients in Q1 respectively (p trend < 0.001). Patients with hs-CRP values in Q3 and Q4 had 1.74 (1.08-2.82) and 2.42 times (1.52-3.87) as high as the risk of death compared with patients in Q1 respectively (p trend < 0.001). Conclusions: Hs-CRP was found to be associated with the incidence of in-hospital HF, HF post-discharge and all-cause mortality in patients with AMI.
Keywords: acute myocardial infarction; heart failure; high sensitivity CRP; mortality; survival.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Wang, Fang and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
D-dimer and the incidence of heart failure and mortality after acute myocardial infarction.Heart. 2021 Feb;107(3):237-244. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2020-316880. Epub 2020 Aug 12. Heart. 2021. PMID: 32788198
-
Biomarker of Collagen Turnover (C-Terminal Telopeptide) and Prognosis in Patients With Non- ST -Elevation Acute Coronary Syndromes.J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 May 7;8(9):e011444. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.011444. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31020897 Free PMC article.
-
High-sensitivity C-reactive protein predicts contrast-induced nephropathy after primary percutaneous coronary intervention.J Nephrol. 2012 May-Jun;25(3):332-40. doi: 10.5301/jn.5000007. J Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 21928234
-
Higher serum phosphorus and calcium levels provide prognostic value in patients with acute myocardial infarction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Sep 7;9:929634. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.929634. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36158790 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of C-reactive protein as an inflammatory and N-terminal probrain natriuretic peptide as a neurohumoral marker in acute heart failure (from the Korean Heart Failure registry).Am J Cardiol. 2014 Feb 1;113(3):511-7. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2013.10.022. Epub 2013 Nov 9. Am J Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24315115
Cited by
-
Ambient Temperature and Cardiac Biomarkers: A Meta-Analysis.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2023;19(6):82-92. doi: 10.2174/1573403X19666230804095744. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37539936 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Pharmacological Implications of Time to Treatment with Interleukin-1 Blockade in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2023 Aug;386(2):156-163. doi: 10.1124/jpet.123.001601. Epub 2023 Apr 10. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2023. PMID: 37037651 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced predictive performance of the GRACE risk score by incorporating lipoprotein(a) for major adverse cardiac events in acute myocardial infarction patients undergoing PCI.Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Risk Prev. 2024 Jul 26;22:200315. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcrp.2024.200315. eCollection 2024 Sep. Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Risk Prev. 2024. PMID: 39157191 Free PMC article.
-
The value of serum Sema4D level in predicting the prognosis of patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and with high thrombus burden.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023 May 3;23(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03244-5. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023. PMID: 37138227 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine to threonine ratio was related to heart failure with reduced or mildly reduced ejection fraction.ESC Heart Fail. 2024 Jun;11(3):1567-1579. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14700. Epub 2024 Feb 15. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 38361178 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lim P, Moutereau S, Simon T, Gallet R, Probst V, Ferrieres J, et al. . Usefulness of fetuin-A and C-reactive protein concentrations for prediction of outcome in acute coronary syndromes (from the French Registry of Acute ST-Elevation Non-ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction [FAST-MI]). Am J Cardiol. (2013) 111:31–7. 10.1016/j.amjcard.2012.08.042 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

