Analysis of epidemiological serosurvey of hepatitis B virus among people under 29 years of age in Jiangsu Province, China
- PMID: 34096830
- PMCID: PMC8437554
- DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2021.1928461
Analysis of epidemiological serosurvey of hepatitis B virus among people under 29 years of age in Jiangsu Province, China
Abstract
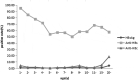
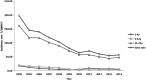
Background: The purpose of this paper was to analyze the prevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), hepatitis B surface antibody (anti-HBs), and hepatitis B core anti-body (anti-HBc)in1-29 years old living in the most populous eastern province of China,22 years after introduction of hepatitis B vaccine (HepB) vaccination of infants and provide provincial baseline data for developping a better prevention and control plan for hepatitis B virus (HBV)in Jiangsu Province, ChinaMethods: The incidence rates of HBV in Jiangsu province from 2004 to 2014 were obtained from the National Notifiable Disease Reporting System (NNDRS). A stratified cluster random sampling method was used to select 3,002 participants aged 1-29 years across 13 HBV monitoring points throughout the province, which had been classified as either urban or rural. HBV serological markers were measured by Abbott microparticle enzyme immunoassay (MEIA) kits (Abbott Laboratories, Chicago, Illinois).Results: The incidence of hepatitis B decreased by approximately 71.44% in Jiangsu province between 2004 and 2014. Serological assessments showed that the prevalence of the HBsAg, anti-HBc, and anti-HBsin the 1-29 age group were 1.20%, 5.33%,and 66.89%, respectively. There was a significantly lower prevalence of HepB who were vaccinated than in unvaccinated subjects (0.46% vs 14.93%, p < .0001). Among these the ages of 1-29, the coverage rate drops from 97.7% to 56.6% with age,andthe timely rate among people aged 1-14 years was 90.93%.Conclusions: Since the HepB was integrated into the immunization programme in Jiangsu province,the rate of hepatitis B reported and the prevalence of HBsAg decreased significantly, and the coverage of HepB and the vaccination rate within 24 hours after birth have played an important role in reducing HBV infection.
Keywords: Hepatitis B; immunization; serosurvey.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The epidemiological characteristics of HBV susceptibility in 1-29 years old young people in China in 2006 and 2014: based on the national sero-survey data analysis].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017 Jul 6;51(7):581-586. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2017.07.002. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28693080 Chinese.
-
[Seroepidemiological analysis of hepatitis B among children aged 1-14 in 3 counties of Guangdong province in 2013].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015 Sep;49(9):777-81. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26733134 Chinese.
-
Significant reduction in notification and seroprevalence rates of hepatitis B virus infection among the population of Zhejiang Province, China, aged between 1 and 29years from 2006 to 2014.Vaccine. 2017 Aug 3;35(34):4355-4361. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2017.06.078. Epub 2017 Jul 4. Vaccine. 2017. PMID: 28687404
-
Long-term impact of infant immunization on hepatitis B prevalence: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Bull World Health Organ. 2018 Jul 1;96(7):484-497. doi: 10.2471/BLT.17.205153. Epub 2018 May 14. Bull World Health Organ. 2018. PMID: 29962551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A meta-analysis of HBsAg-positive rate among general Chinese populations aged 1--59 years.Infect Dis (Lond). 2015;47(12):878-88. doi: 10.3109/23744235.2015.1064541. Epub 2015 Aug 24. Infect Dis (Lond). 2015. PMID: 26305713 Review.
Cited by
-
Trends in disease burden of hepatitis B infection in Jiangsu Province, China, 1990-2021.Infect Dis Model. 2023 Jul 10;8(3):832-841. doi: 10.1016/j.idm.2023.07.007. eCollection 2023 Sep. Infect Dis Model. 2023. PMID: 37520113 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B virus infection among the tribal and particularly vulnerable tribal population from an eastern state of India: Findings from the serosurvey in seven tribal dominated districts, 2021-2022.Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 6;14:1039696. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1039696. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36950163 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B prevalence in pregnant women in China: Progress and realities.Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2021 Oct 21;16:100289. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2021.100289. eCollection 2021 Nov. Lancet Reg Health West Pac. 2021. PMID: 34881373 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wang FZ, Cui FQ. The immunoprophylaxis strategy of prevention mother to child transmission of hepatitis B virus (in Chinese). Chin J Vaccines Immunization. 2014;20:355–59.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical