Site-specific glycoproteomic analysis revealing increased core-fucosylation on FOLR1 enhances folate uptake capacity of HCC cells to promote EMT
- PMID: 34093861
- PMCID: PMC8171077
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.56882
Site-specific glycoproteomic analysis revealing increased core-fucosylation on FOLR1 enhances folate uptake capacity of HCC cells to promote EMT
Abstract
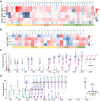
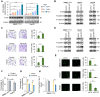
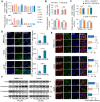
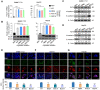
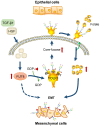
Rationale: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) has been recognized as an important step toward high invasion and metastasis of many cancers including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), while the mechanism for EMT promotion is still ambiguous. Methods: The dynamic alterations of site-specific glycosylation during HGF/TGF-β1-induced EMT process of three HCC cell lines were systematically investigated using precision glycoproteomic methods. The possible roles of EMT-related glycoproteins and site-specific glycans were further confirmed by various molecular biological approaches. Results: Using mass spectrometry-based glycoproteomic methods, we totally identified 2306 unique intact glycopeptides from SMMC-7721 and HepG2 cell lines, and found that core-fucosylated glycans were accounted for the largest proportion of complex N-glycans. Through quantification analysis of intact glycopeptides, we found that the majority of core-fucosylated intact glycopeptides from folate receptor α (FOLR1) were up-regulated in the three HGF-treated cell lines. Similarly, core-fucosylation of FOLR1 were up-regulated in SMMC-7721 and Hep3B cells with TGF-β1 treatment. Using molecular approaches, we further demonstrated that FUT8 was a driver for HGF/TGF-β1-induced EMT. The silencing of FUT8 reduced core-fucosylation and partially blocked the progress of HGF-induced EMT. Finally, we confirmed that the level of core-fucosylation on FOLR1 especially at the glycosite Asn-201 positively regulated the cellular uptake capacity of folates, and enhanced uptake of folates could promote the EMT of HCC cells. Conclusions: Based on the results, we proposed a potential pathway for HGF or TGF-β1-induced EMT of HCC cells: HGF or TGF-β1 treatment of HCC cells can increase the expression of glycosyltransferase FUT8 to up-regulate the core-fucosylation of N-glycans on glycoproteins including the FOLR1; core-fucosylation on FOLR1 can then enhance the folate uptake capacity to finally promote the EMT progress of HCC cells.
Keywords: FOLR1; core-fucosylation; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; glycoproteome; hepatocellular carcinoma.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures


Similar articles
-
FUT8 promotes breast cancer cell invasiveness by remodeling TGF-β receptor core fucosylation.Breast Cancer Res. 2017 Oct 5;19(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s13058-017-0904-8. Breast Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28982386 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking core fucosylation of TGF-β1 receptors downregulates their functions and attenuates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of renal tubular cells.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011 Apr;300(4):F1017-25. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00426.2010. Epub 2011 Jan 12. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21228108
-
STAT3 aggravates TGF-β1-induced hepatic epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and migration.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Feb;98:214-221. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.12.035. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29268242
-
Glycoproteomic markers of hepatocellular carcinoma-mass spectrometry based approaches.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2019 May;38(3):265-290. doi: 10.1002/mas.21583. Epub 2018 Nov 25. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2019. PMID: 30472795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
True significance of N-acetylglucosaminyltransferases GnT-III, V and α1,6 fucosyltransferase in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer.Mol Aspects Med. 2021 Jun;79:100905. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2020.100905. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Mol Aspects Med. 2021. PMID: 33010941 Review.
Cited by
-
Strategies for Proteome-Wide Quantification of Glycosylation Macro- and Micro-Heterogeneity.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 30;23(3):1609. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031609. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tools to cut the sweet layer-cake that is glycoproteomics.Nat Methods. 2021 Sep;18(9):991-995. doi: 10.1038/s41592-021-01253-w. Nat Methods. 2021. PMID: 34404955 Free PMC article.
-
Glycosylation and its research progress in endometrial cancer.Clin Transl Oncol. 2022 Oct;24(10):1865-1880. doi: 10.1007/s12094-022-02858-z. Epub 2022 Jun 25. Clin Transl Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35752750 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Computational and Chemical Design Strategy for Manipulating Glycan-Protein Recognition.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Jun;11(24):e2308522. doi: 10.1002/advs.202308522. Epub 2024 Apr 6. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38582526 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical glycoproteomics: methods and diseases.MedComm (2020). 2024 Oct 4;5(10):e760. doi: 10.1002/mco2.760. eCollection 2024 Oct. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39372389 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Giannelli G, Koudelkova P, Dituri F, Mikulits W. Role of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2016;65:798–808. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

