Effects of Salvia miltiorrhiza extract on lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 34093750
- PMCID: PMC8170645
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.10226
Effects of Salvia miltiorrhiza extract on lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
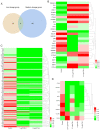
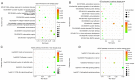
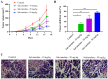
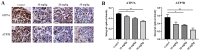
Lung adenocarcinoma is the most common subtype of non-small cell lung carcinoma. Tanshinone I is an important fat-soluble component in the extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza that has been reported to inhibit lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation. However, no studies have clearly demonstrated changes in lung adenocarcinoma gene expression and signaling pathway enrichment following Tanshinone I treatment. And it remains unclear whether salvianolate has an effect on lung adenocarcinoma. The present study downloaded the GSE9315 dataset from the Gene Expression Omnibus database to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and the underlying signaling pathways involved after Tanshinone I administration in the lung adenocarcinoma cell line CL1-5. The results revealed that there were 28 and 102 DEGs in the low dosage group (0.01 and 0.10 µg/ml Tanshinone I) and medium dosage groups (1 and 10 µg/ml Tanshinone I), respectively. In the low dosage group, DEGs were mainly enriched in 'positive regulation of T-helper cell differentiation' and 'protein complex'. In the medium dosage group, 102 DEGs were enriched in 'MAPK cascade' and 'extracellular exosome'. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis demonstrated enrichment of both groups in the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Furthermore, there were nine overlapping DEGs [ADP ribosylation factor-interacting protein 2, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 6, SH2 domain-containing adaptor protein B, Src homology 2 domain-containing transforming protein1, collagen type VI α1 chain, elastin, integrin subunit α, endoplasmic reticulum mannosyl-oligosaccharide 1,2-α-mannosidase and sterile α motif domain-containing 9 like] between the two groups, which serve to be potential targets for the treatment of lung adenocarcinoma. The present study also investigated the possible effects of salvianolate on lung adenocarcinoma in vivo using nude mouse xenograft models injected with the A549 cell line. The data revealed that salvianolate not only suppressed lung adenocarcinoma tumor growth of in nude mice, but also downregulated the expression levels of ATP7A and ATP7B, which are important proteins in the tumorigenesis and chemotherapy of lung adenocarcinoma. The present study provided evidence for the potential use of Salvia miltiorrhiza extract for treating lung adenocarcinomas in the clinic.
Keywords: anticancer effect; differentially expressed genes; lung adenocarcinoma; salvianolate; tanshinone I.
Copyright: © Tian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Apoptosis induced by the methanol extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge in non-small cell lung cancer through PTEN-mediated inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2017 Mar 22;200:107-116. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.12.051. Epub 2017 Jan 12. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28088493
-
Anticancer effects of tanshinone I in human non-small cell lung cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Nov;7(11):3527-38. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-2288. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008. PMID: 19001436
-
Identification of differentially expressed genes between lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma by gene expression profiling.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Aug;14(2):1483-90. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5420. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27356570 Free PMC article.
-
[Anti-inflammatory constituents, aloesin and aloemannan in Aloe species and effects of tanshinon VI in Salvia miltiorrhiza on heart].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2003 Jul;123(7):517-32. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.123.517. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2003. PMID: 12875235 Review. Japanese.
-
Salvia miltiorrhiza in Treating Cardiovascular Diseases: A Review on Its Pharmacological and Clinical Applications.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jul 5;10:753. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00753. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31338034 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Salviae miltiorrhiza against human lung cancer: A review of its mechanism (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2023 Feb 13;25(3):139. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.11838. eCollection 2023 Mar. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 36845955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salvia miltiorrhiza in cancer: Potential role in regulating MicroRNAs and epigenetic enzymes.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 12;13:1008222. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1008222. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36172186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curcumin suppresses copper accumulation in non-small cell lung cancer by binding ATOX1.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2024 Aug 21;25(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s40360-024-00784-0. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39169392 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization: Cancer Today. 2021. Accessed from https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
