Inflammatory bowel disease in Tuzla Canton, Bosnia-Herzegovina: A prospective 10-year follow-up
- PMID: 34092980
- PMCID: PMC8160617
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i20.2630
Inflammatory bowel disease in Tuzla Canton, Bosnia-Herzegovina: A prospective 10-year follow-up
Abstract
Background: The incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) vary between regions but have risen globally in recent decades. A lack of data from developing nations limits the understanding of IBD epidemiology.
Aim: To perform a follow-up review of IBD epidemiology in the Tuzla Canton of Bosnia-Herzegovina during a 10-year period (2009-2019).
Methods: We prospectively evaluated the hospital records of both IBD inpatients and outpatients residing in Tuzla Canton for the specified period of time between January 1, 2009 and December 31, 2019. Since all our patients had undergone proximal and distal endoscopic evaluations at the hospital endoscopy unit, we used the hospital's database as a primary data source, alongside an additional cross-relational search of the database. Both adult and pediatric patients were included in the study. Patients were grouped by IBD type, phenotype, age, and gender. Incidence rates were calculated with age standardization using the European standard population. Trends in incidence and prevalence were evaluated as a 3-year moving average and average annual percentage change rates.
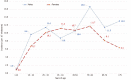
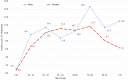
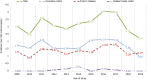
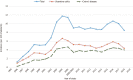
Results: During the 10-year follow-up period, 651 patients diagnosed with IBD were monitored (of whom 334, or 51.3%, were males, and 317, or 48.7%, were females). Of all the patients, 346 (53.1%) had been diagnosed with ulcerative colitis (UC), 292 (44.9%) with Crohn's disease (CD), and 13 (2%) with indeterminate colitis (IC). We observed 440 newly diagnosed patients with IBD: 240 (54.5%) with UC, 190 (43.2%) with CD, and 10 (2.3%) with IC. The mean annual crude incidence rates were found to be 9.01/100000 population for IBD [95% confidence interval (CI): 8.17-9.85], with 4.91/100000 (95%CI: 4.29-5.54) for UC and 3.89/100000 (95%CI: 3.34-4.44) for CD. Calculated IBD prevalence in 2019 was 146.64/100000 (95%CI: 128.09-165.19), with 77.94/100000 (95%CI: 68.08-87.70) for UC and 65.77/100000 (95%CI: 54.45-74.1) for CD. The average annual IBD percentage change was 0.79% (95%CI: 0.60-0.88), with -2.82% (95%CI: -2.67 to -2.97) for UC and 6.92% (95%CI: 6.64-7.20) for CD. During the study period, 24,509 distal endoscopic procedures were performed. The incidence of IBD was 3.16/100 examinations (95%CI: 2.86-3.45) or 1.72/100 examinations (95%CI: 1.5-1.94) for UC and 1.36/100 examinations (95%CI: 1.17-1.56) for CD.
Conclusion: Trends in the incidence and prevalence of IBD in Tuzla Canton are similar to Eastern European averages, although there are significant epidemiological differences within geographically close and demographically similar areas.
Keywords: Crohn's disease; Endoscopy; Epidemiology; Indeterminate colitis; Inflammatory bowel disease; Ulcerative colitis.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest related to this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ulcerative colitis in the Tuzla region of Bosnia and Herzegovina between 1995 and 2006: epidemiological and clinical characteristics.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010 Mar;22(3):346-53. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e32832bfe05. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010. PMID: 19474740
-
Crohn's disease in Tuzla region of Bosnia and Herzegovina: a 12-year study (1995-2006).Int J Colorectal Dis. 2008 Oct;23(10):957-64. doi: 10.1007/s00384-008-0493-1. Epub 2008 Jun 12. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2008. PMID: 18548259
-
Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Occurrence, course and prognosis during the first year of disease in a European population-based inception cohort.Dan Med J. 2014 Jan;61(1):B4778. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 24393595
-
Differentiating ulcerative colitis from Crohn disease in children and young adults: report of a working group of the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition and the Crohn's and Colitis Foundation of America.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007 May;44(5):653-74. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e31805563f3. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2007. PMID: 17460505
-
Natural history of pediatric-onset inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review.J Clin Gastroenterol. 2012 Aug;46(7):581-9. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e318247c32f. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2012. PMID: 22772738 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Short-term efficacy of vedolizumab in patients with inflammatory bowel disease in real-life settings in Bosnia and Herzegovina.Biomol Biomed. 2024 Sep 6;24(5):1400-1406. doi: 10.17305/bb.2024.10433. Biomol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38683174 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Feldman M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ. Sleisenger and Fordtran's gastrointestinal and liver disease: Pathophysiology/diagnosis/management. 10th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders/Elsevier, 2016: 115-116.
-
- Loftus EV Jr. Clinical epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease: Incidence, prevalence, and environmental influences. Gastroenterology. 2004;126:1504–1517. - PubMed
-
- Burisch J, Pedersen N, Čuković-Čavka S, Brinar M, Kaimakliotis I, Duricova D, Shonová O, Vind I, Avnstrøm S, Thorsgaard N, Andersen V, Krabbe S, Dahlerup JF, Salupere R, Nielsen KR, Olsen J, Manninen P, Collin P, Tsianos EV, Katsanos KH, Ladefoged K, Lakatos L, Björnsson E, Ragnarsson G, Bailey Y, Odes S, Schwartz D, Martinato M, Lupinacci G, Milla M, De Padova A, D'Incà R, Beltrami M, Kupcinskas L, Kiudelis G, Turcan S, Tighineanu O, Mihu I, Magro F, Barros LF, Goldis A, Lazar D, Belousova E, Nikulina I, Hernandez V, Martinez-Ares D, Almer S, Zhulina Y, Halfvarson J, Arebi N, Sebastian S, Lakatos PL, Langholz E, Munkholm P EpiCom-group. East-West gradient in the incidence of inflammatory bowel disease in Europe: the ECCO-EpiCom inception cohort. Gut. 2014;63:588–597. - PubMed
-
- Ng SC, Shi HY, Hamidi N, Underwood FE, Tang W, Benchimol EI, Panaccione R, Ghosh S, Wu JCY, Chan FKL, Sung JJY, Kaplan GG. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet. 2017;390:2769–2778. - PubMed
-
- Sincić BM, Vucelić B, Persić M, Brncić N, Erzen DJ, Radaković B, Mićović V, Stimac D. Incidence of inflammatory bowel disease in Primorsko-goranska County, Croatia, 2000-2004: A prospective population-based study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2006;41:437–444. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

