The Effects of a 7000-Step Goal and Weekly Group Walking Program for Overweight and Obese Elderly People in Sarawak, Malaysia: A Quasi-experimental Study
- PMID: 34092066
- PMCID: PMC8190551
- DOI: 10.3961/jpmph.20.584
The Effects of a 7000-Step Goal and Weekly Group Walking Program for Overweight and Obese Elderly People in Sarawak, Malaysia: A Quasi-experimental Study
Abstract
Objectives: Physical inactivity is the fourth leading global risk factor for mortality, followed by obesity. The combination of these risk factors is associated with non-communicable diseases, impaired physical function, and declining mental function. The World Health Organization recommends physical activity to reduce the mortality rate. Thus, this study examined the effects on anthropometric measurements of a 12-week walking program for elderly people in Samarahan, Sarawak, Malaysia with a 7000-step goal and weekly group walking activities.
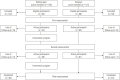
Methods: A quasi-experimental study was conducted involving 109 elderly people with a body mass index (BMI) ≥25.0 kg/m2. BMI, body composition, and average daily steps were measured at baseline, 6 weeks, and 12 weeks. Data were analyzed using SPSS version 26.0, and repeated-measures analysis of variance with the paired t-test for post-hoc analysis was conducted.
Results: In total, 48 participants in the intervention group and 61 participants in the control group completed the study. A significant interaction was found between time and group. The post-hoc analysis showed a significant difference between pre-intervention and post-intervention (within the intervention group). The post-intervention analysis revealed an increase in the mean number of daily steps by 3571.59, with decreases in body weight (-2.20 kg), BMI (-0.94 kg/m2), body fat percentage (-3.52%), visceral fat percentage (-1.29%) and waist circumference (-2.91 cm). Skeletal muscle percentage also showed a significant increase (1.67%).
Conclusions: A 12-week walking program combining a 7000-step goals with weekly group walking activities had a significant effect on the anthropometric measurements of previously inactive and overweight/obese elderly people.
Keywords: Body composition; Elderly; Malaysia; Physical activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest associated with the material presented in this paper.
Similar articles
-
[Effects of short-term intervention of walking on body mass index, waist circumference, and related indicators of working population].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019 Feb 6;53(2):212-217. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2019.02.017. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30744299 Chinese.
-
The effectiveness of web-based programs on the reduction of childhood obesity in school-aged children: A systematic review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012;10(42 Suppl):1-14. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2012-248. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 27820152
-
Effect of 12-Week Interventions Involving Nordic Walking Exercise and a Modified Diet on the Anthropometric Parameters and Blood Lipid Profiles in Overweight and Obese Ex-Coal Miners.Obes Facts. 2020;13(2):201-212. doi: 10.1159/000506403. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Obes Facts. 2020. PMID: 32209798 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of Exercise Intervention for Weight Loss in Overweight and Obese Adolescents: Meta-Analysis and Implications.Sports Med. 2016 Nov;46(11):1737-1751. doi: 10.1007/s40279-016-0537-6. Sports Med. 2016. PMID: 27139723 Review.
-
Offspring body size and metabolic profile - effects of lifestyle intervention in obese pregnant women.Dan Med J. 2014 Jul;61(7):B4893. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25123127 Review.
Cited by
-
Socio-demographic Determinants of Low Physical Activity in Peruvian Adults: Results of a Population-based Survey Performed in 2017-2018.J Prev Med Public Health. 2021 Nov;54(6):461-470. doi: 10.3961/jpmph.21.418. Epub 2021 Nov 7. J Prev Med Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34875829 Free PMC article.
-
Promoting Physical Activity in Older Adults With Type 2 Diabetes via an Anthropomorphic Conversational Agent: Development of an Evidence and Theory-Based Multi-Behavior Intervention.Front Psychol. 2022 Jul 12;13:883354. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.883354. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35903740 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of Physical Activity Intervention Programs in ASEAN Countries: Efficacy and Future Directions.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Apr 28;19(9):5357. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19095357. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35564751 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization Physical activity. [cited 2020 May 20]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/physical-activity.
-
- World Health Organization Controlling the global obesity epidemic . [cited 2020 Nov 26]. Available from: https://www.who.int/activities/controlling-the-global-obesity-epidemic.
-
- Institute for Public Health. National Institutes of Health (NIH) Ministry of Health Malaysia National Health and Morbidity Survey (NHMS) 2018: elderly health. [cited 2020 Nov 26]. Available from: http://iku.moh.gov.my/images/IKU/Document/REPORT/NHMS2018/NHMS2018Elderl....
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources