Potential Impact of ALKBH5 and YTHDF1 on Tumor Immunity in Colon Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 34079761
- PMCID: PMC8165310
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.670490
Potential Impact of ALKBH5 and YTHDF1 on Tumor Immunity in Colon Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
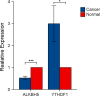
Background: ALKBH5 and YTHDF1 are regarded as the eraser and reader, respectively, in N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification. Recently, immune contexture has been drawing increasing attention in terms of the progression and treatment of cancers. This study aimed to determine the relationship between ALKBH5/YTHDF1 and immunological characteristics of colon adenocarcinoma (COAD).
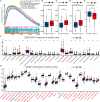
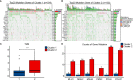
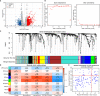
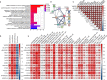
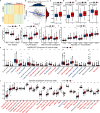
Methods: Expression of ALKBH5 and YTHDF1 was investigated across TCGA and GEO validated in our study. Patients with COAD were divided into two clusters using consensus clustering based on the expression of ALKBH5 and YTHDF1. We then compared their clinical characteristics and performed gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) to identify the functional differences. Immune infiltration analyses were conducted using ESTIMATE, CIBERSORT, and ssGSEA. In addition, we evaluated the expression of the targets of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) and calculated the tumor mutation burden (TMB) of the tumor samples. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) was used to identify the genes related to both ALKBH5/YTHDF1 expression and immunity. GSE39582 was utilized for external validation of immunological features between the two clusters.
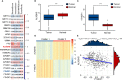
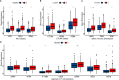
Results: Cluster 2 had high expression of ALKBH5 and lesser so of YTHDF1, whereas Cluster 1 had just the reverse. Cluster 1 had a higher N stage and pathological stage than Cluster 2. The latter had stronger immune infiltration, higher expression of targets of ICIs, more TMB, and a larger proportion of deficiency in mismatch repair-microsatellite instability-high (dMMR-MSI-H) status than Cluster 1. Moreover, WGCNA revealed 14 genes, including PD1 and LAG3, related to both the expression of ALKBH5/YTHDF1 and immune scores.
Conclusions: ALKBH5 and YTHDF1 influence immune contexture and can potentially transform cold tumors into hot tumors in patients with COAD.
Keywords: ALKBH5; YTHDF1; colon adenocarcinoma; immune contexture; m6A modification.
Copyright © 2021 Yan, An, Xu, Wang, Sun and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential impact of WTAP and YTHDF2 on tumor immunity in lung adenocarcinoma.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Nov 11;101(45):e31195. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031195. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36397411 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Two m6A Readers YTHDF1 and IGF2BP2 as Immune Biomarkers in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Genet. 2022 May 12;13:903634. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.903634. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35646049 Free PMC article.
-
N6-Methyladenosine Modification Patterns and Tumor Microenvironment Immune Characteristics Associated With Clinical Prognosis Analysis in Stomach Adenocarcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jun 15;10:913307. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.913307. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35813200 Free PMC article.
-
The roles and mechanisms of the m6A reader protein YTHDF1 in tumor biology and human diseases.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Nov 4;26:1270-1279. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.10.023. eCollection 2021 Dec 3. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 34853726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Roles of RNA N6-Methyladenosine in Urological Tumors.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Sep 9;8:579919. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.579919. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33015074 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Analysis of Cell Mixtures Deconvolution and Gene Signatures Generated for Blood, Immune and Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 28;24(13):10765. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310765. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445946 Free PMC article.
-
N6-Methyladenosine RNA-Binding Protein YTHDF1 in Gastrointestinal Cancers: Function, Molecular Mechanism and Clinical Implication.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 18;14(14):3489. doi: 10.3390/cancers14143489. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated analysis of potential gene crosstalk between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetic nephropathy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 25;13:1032814. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1032814. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36387855 Free PMC article.
-
Influencing immunity: role of extracellular vesicles in tumor immune checkpoint dynamics.Exp Mol Med. 2024 Nov;56(11):2365-2381. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01340-w. Epub 2024 Nov 11. Exp Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39528800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CHSY3 promotes proliferation and migration in gastric cancer and is associated with immune infiltration.J Transl Med. 2023 Jul 17;21(1):474. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04333-x. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37461041 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

